Log Configurations
By default, the logging level for Spark applications is set to INFO, which provides a good balance between useful information and minimal log verbosity. However, users may need to adjust the log level or customize the logging configuration to suit specific operational needs.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide on how to control the log level of Spark jobs and configure a custom log4j2 logging configuration using the IOMETE Console. It includes instructions for setting the log level globally via the Helm chart, configuring custom log4j2 properties, and dynamically controlling the log level using environment variables.
1. Global Log Level Configuration
By default, the log level for all Spark applications deployed on the IOMETE Platform is set to INFO. This global configuration can be modified during the deployment of the data-plane instance by adjusting the Helm chart.
Steps to Set Global Log Level:
- Locate the Helm Chart: When deploying the data-plane instance, find the
values.yamlfile in the Helm chart. - Modify the Log Level: Set the desired log level in the
sparksection of thevalues.yamlfile as shown below:Replacespark:
logLevel: infoinfowith the desired log level (e.g.,debug,warn,error).
2. Custom Log Configurations
Individual Spark jobs may require different logging levels or configurations. The IOMETE Platform allows users to define custom log configurations by providing a log4j2 properties file and setting the log level dynamically using environment variables.
Using Custom log4j2 Configuration
Users can provide a custom log4j2 configuration file when deploying Spark jobs through the IOMETE Console. This custom configuration file can be used to define detailed logging behavior for specific jobs.
Steps to Configure Custom log4j2 File:
- Open the Spark Job's configuration page in the IOMETE Console.
- Navigate to the Config Maps section and create a new Config Map containing your custom
log4j2.propertiesfile. - Specify the file path and name. For example,
/etc/configs/log4j2.properties.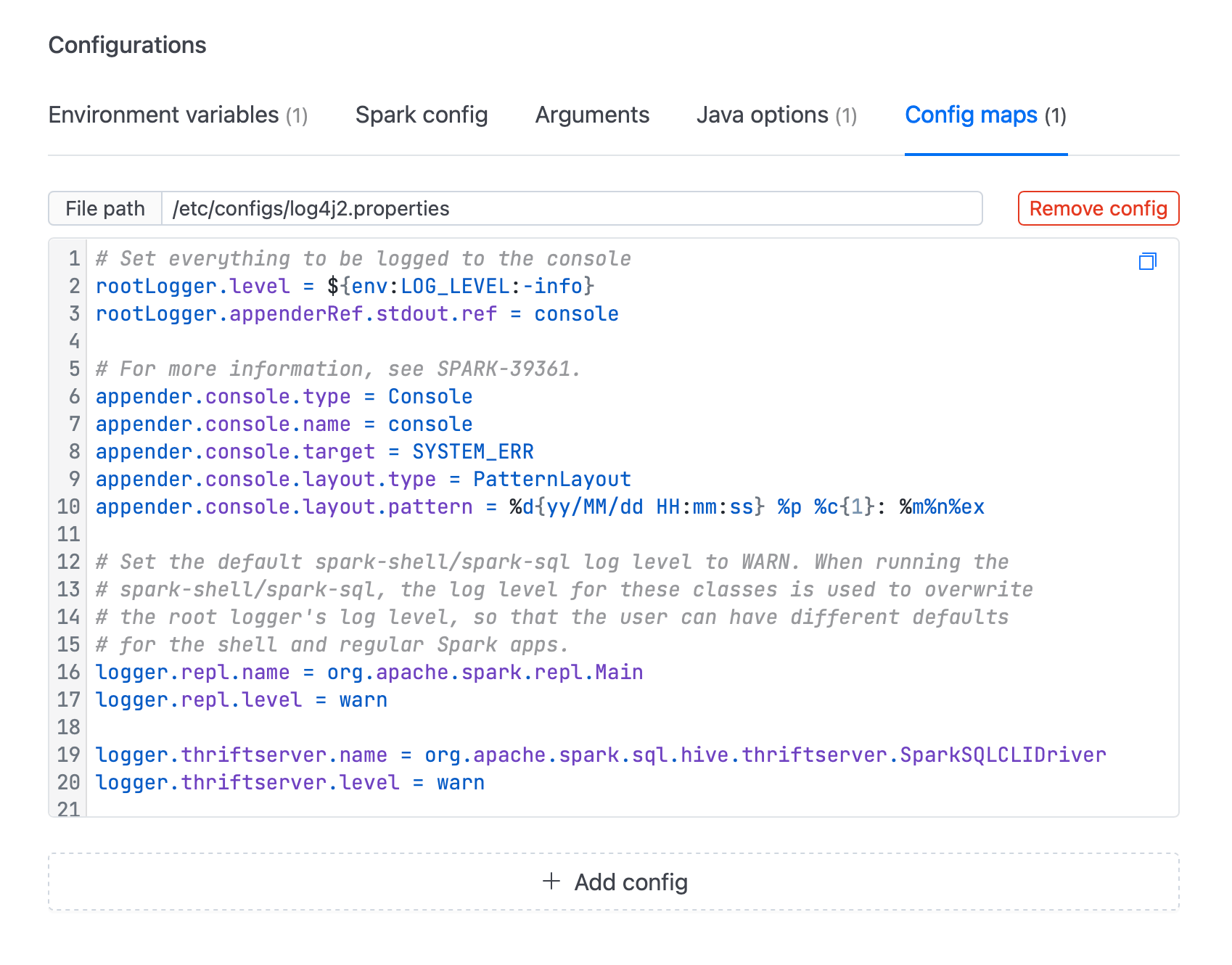

- Add the following Java option to specify the path to the custom log4j2 configuration file:
Make sure the path corresponds to where the Config Map is mounted within the container.
-Dlog4j.configurationFile=/etc/configs/log4j2.properties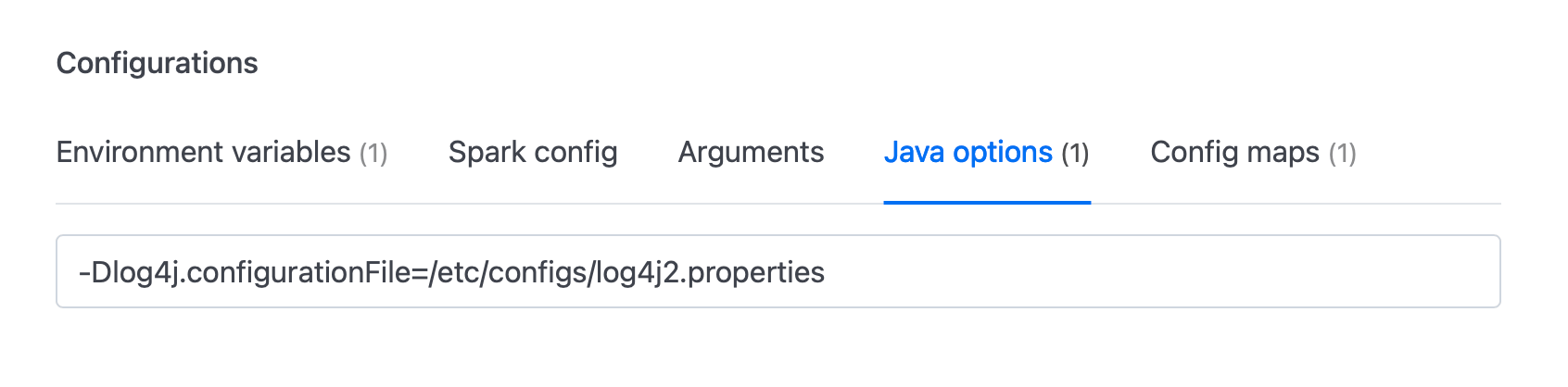

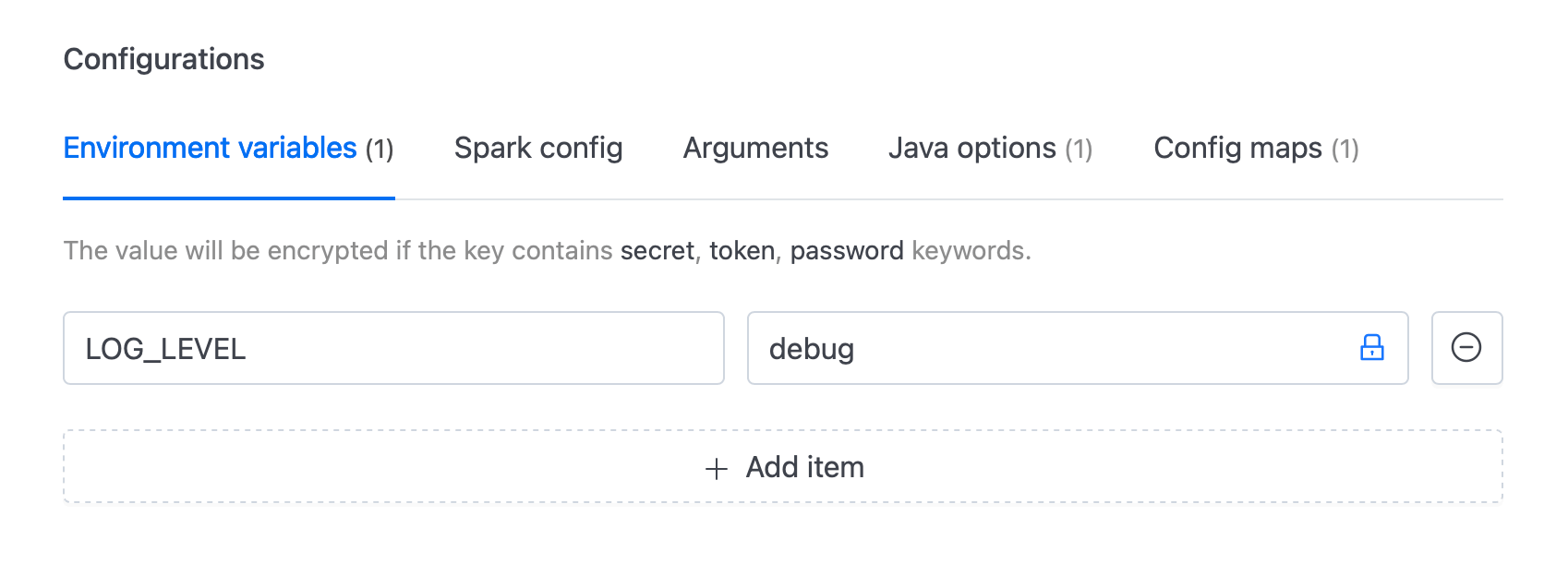
Setting Log Level Using Environment Variables
For more flexibility, users can dynamically set the log level using environment variables. The log level can be defined in the log4j2.properties file using the ${env:LOG_LEVEL:-info} placeholder (as in the screenshot above), which allows the log level to be passed at runtime through environment variables.
Example log4j2.properties Configuration:
rootLogger.level = ${env:LOG_LEVEL:-info}
rootLogger.appenderRef.stdout.ref = console
# Console appender configuration
appender.console.type = Console
appender.console.name = console
appender.console.target = SYSTEM_ERR
appender.console.layout.type = PatternLayout
appender.console.layout.pattern = %d{yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss} %p %c{1}: %m%n%ex
# Other logger configurations...
In the IOMETE Console, when configuring the Spark job, navigate to the Environment Variables section and define LOG_LEVEL with the desired log level (e.g., debug, warn).

3. Base log4j2 Configuration Template
Below is a base template for the log4j2.properties file. This template can be customized as needed for specific logging requirements.
# Set everything to be logged to the console
rootLogger.level = ${env:LOG_LEVEL:-info}
rootLogger.appenderRef.stdout.ref = console
# Console appender configuration
appender.console.type = Console
appender.console.name = console
appender.console.target = SYSTEM_ERR
appender.console.layout.type = PatternLayout
appender.console.layout.pattern = %d{yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss} %p %c{1}: %m%n%ex
# Default log levels for Spark REPL and SQL shell
logger.repl.name = org.apache.spark.repl.Main
logger.repl.level = warn
logger.thriftserver.name = org.apache.spark.sql.hive.thriftserver.SparkSQLCLIDriver
logger.thriftserver.level = warn
# Settings to quiet third-party logs
logger.jetty1.name = org.sparkproject.jetty
logger.jetty1.level = warn
logger.jetty2.name = org.sparkproject.jetty.util.component.AbstractLifeCycle
logger.jetty2.level = error
logger.replexprTyper.name = org.apache.spark.repl.SparkIMain$exprTyper
logger.replexprTyper.level = info
logger.replSparkILoopInterpreter.name = org.apache.spark.repl.SparkILoop$SparkILoopInterpreter
logger.replSparkILoopInterpreter.level = info
logger.parquet1.name = org.apache.parquet
logger.parquet1.level = error
logger.parquet2.name = parquet
logger.parquet2.level = error
# Hive support and ThriftServer log settings
logger.RetryingHMSHandler.name = org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.RetryingHMSHandler
logger.RetryingHMSHandler.level = fatal
logger.FunctionRegistry.name = org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.FunctionRegistry
logger.FunctionRegistry.level = error
# ThriftServer log suppression
appender.console.filter.1.type = RegexFilter
appender.console.filter.1.regex = .*Thrift error occurred during processing of message.*
appender.console.filter.1.onMatch = deny
appender.console.filter.1.onMismatch = neutral
Troubleshooting
SLF4J StaticLoggerBinder Warning
When running Spark applications, you may encounter the following warning messages related to SLF4J
SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
This warning only happens in slf4j version 1.7.x (and earlier versions) and it indicates that the SLF4J binding is not found in the classpath. Which happens due to conflicting dependencies. By default Spark uses the slf4j version 2.0.x. To resolve this issue you can force spark to load the version 2.0.x before the other conflicting dependencies. You can do this by adding the following spark-conf configuration:
spark.driver.extraClassPath /opt/spark/jars/slf4j-api-2.0.7.jar