Job Orchestrator
Overview
The Job Orchestrator is a new addition to IOMETE’s job management platform, designed to enable
- Priority-based scheduling: Prioritize business-critical jobs over routine workloads.
- Resource-aware execution: Submit jobs only when sufficient cluster resources are available.
- Built-in observability: Gain real-time visibility into job execution and resource usage.
Key Features
Priority-Aware Scheduling
Easily configure job priority (High vs Normal) to ensure critical jobs are executed first. The system maintains separate queues for each priority level, with high-priority jobs always processed before normal-priority ones.
Resource-Aware Execution
Jobs are submitted only when cluster capacity is available, reducing the chances of failure due to insufficient compute resources. The orchestrator continuously monitors CPU & memory availability before scheduling job execution.
FIFO Queue Processing
Within each priority level, jobs are processed in First-In-First-Out (FIFO) order. The system will process the first job in the queue completely before moving to the next job, even if resources are available for subsequent jobs.
Queue behavior:
- High-priority queue is always processed before normal-priority queue.
- Within each queue, jobs execute in the order they were submitted.
- If the first job in queue cannot run due to resource constraints, subsequent jobs wait until resources become available or the blocking job completes.
Integrated Monitoring
Includes a Prometheus exporter and ready-to-use Grafana dashboard to track:
- Cluster usage trends per namespace, domain, priority & job.
- Job wait times by priority level.
- Resource allocation patterns.
Flexible Enable/Disable Options
You can opt in or out at the system level or individual job level, allowing gradual migration and testing.
Using the New Flow
How to Enable
Enable First at the System Level
In your Helm values.yaml, enable the feature:
features:
jobOrchestrator:
enabled: true
This will deploy the orchestrator server, workers, and metrics exporter components across your IOMETE deployment.
Then at a Job Level
- Navigate to Spark Jobs and create a new job or configure an existing one.
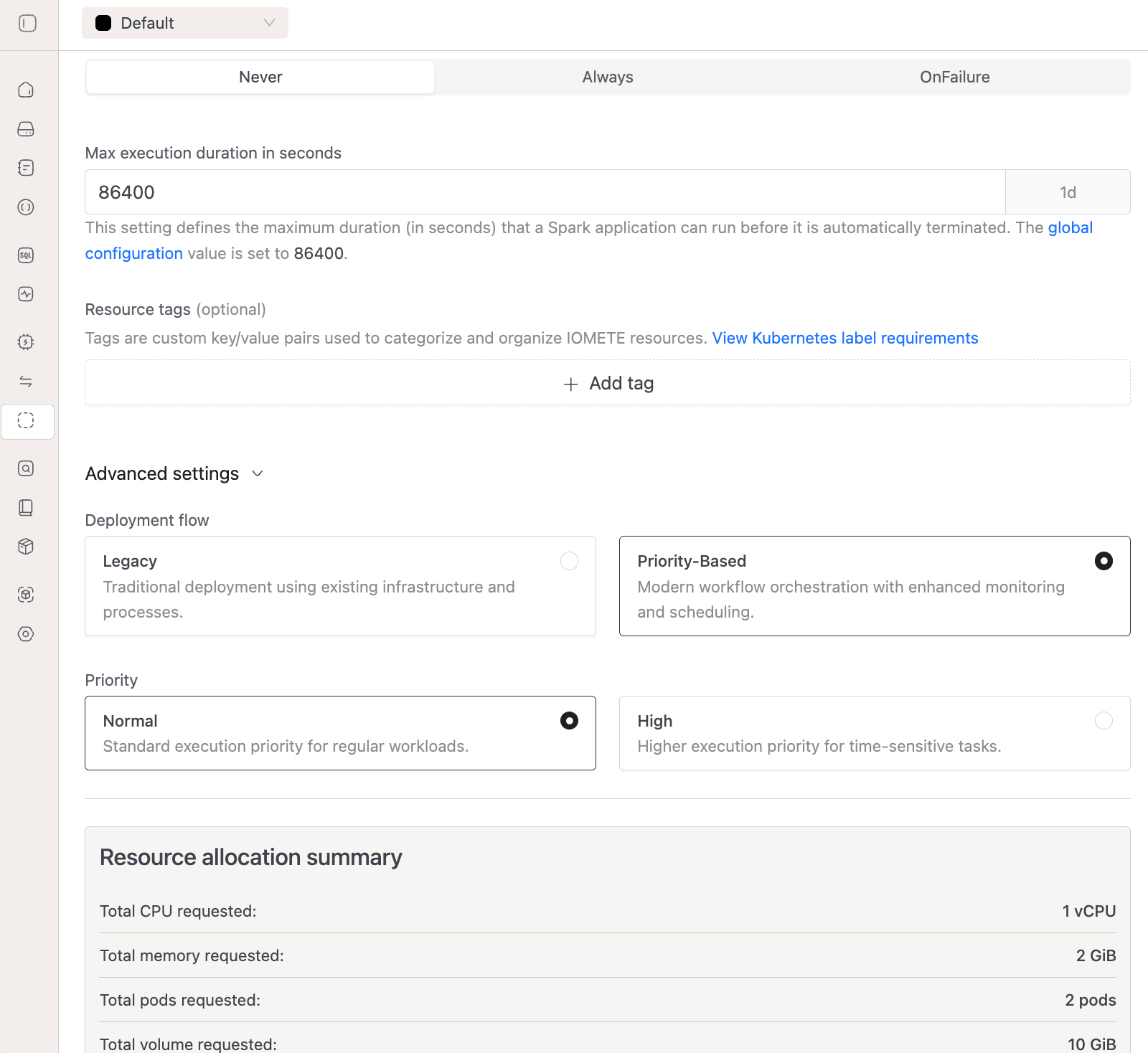
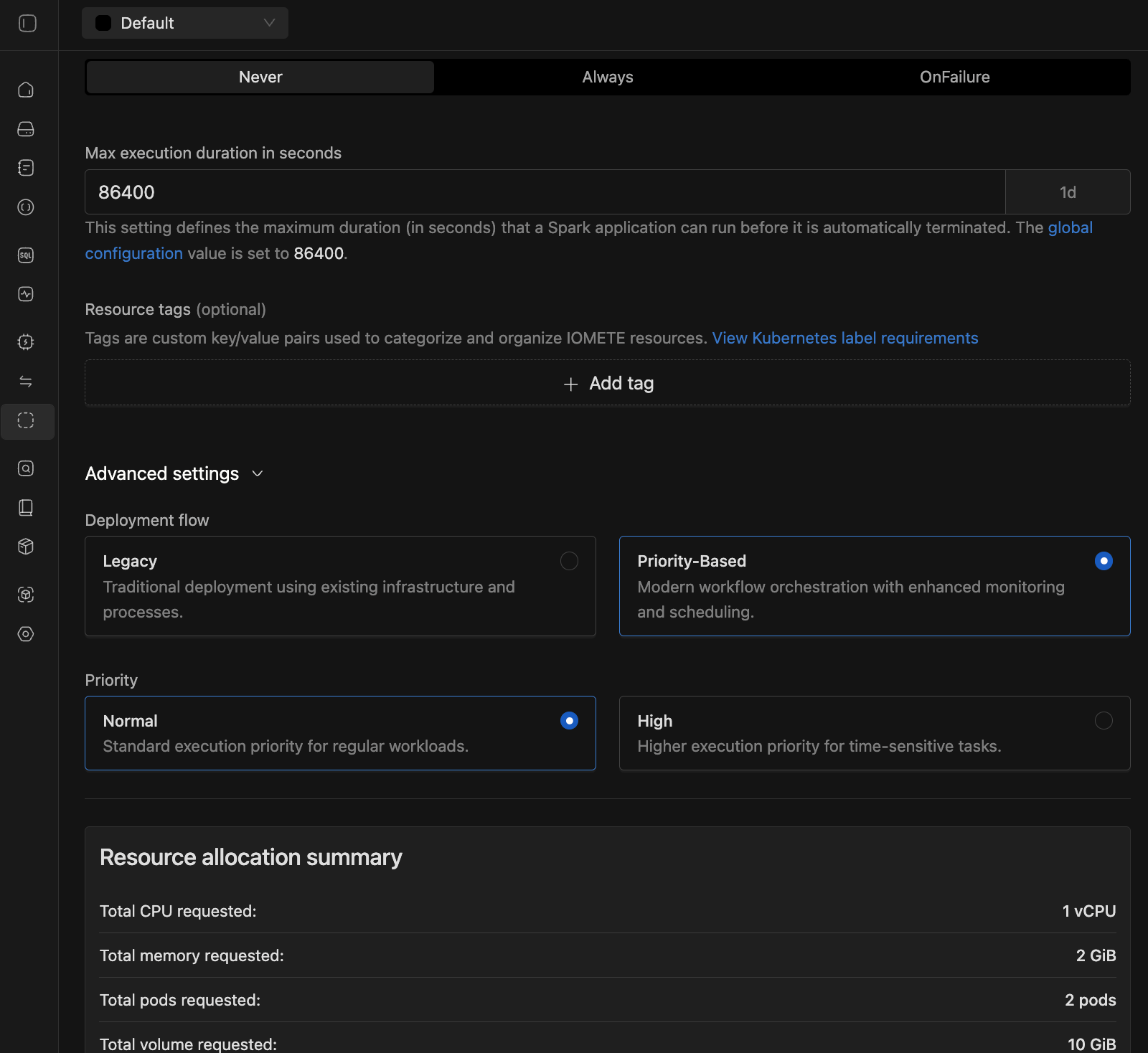
- Go to Advanced Settings section
- Change Deployment Flow from
LegacytoPriority-Based - Select your Priority:
- High - for time-sensitive, business-critical tasks
- Normal - for regular data processing workloads
Start by testing the orchestrator with non-critical jobs before migrating production workloads.
How to Disable
At the job level
Change Deployment Flow back to Legacy in the job's advanced settings to opt out of orchestration for specific jobs.
At the system level
Set features.jobOrchestrator.enabled: false in your Helm values to disable orchestration platform-wide.
Before disabling the flag, please move all jobs back to the Legacy flow at once by using this API endpoint:
curl --location 'https://<IOMETE_URL>/api/v1/domains/<DOMAIN_NAME>/spark/jobs/migrate-from-prefect' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN>' \
--data '{}'
Please replace:
<IOMETE_URL>with your actual IOMETE instance URL<DOMAIN_NAME>with the actual domain name<TOKEN>with your authentication token
Configuration
Helm Chart Settings
Configure orchestrator settings in your values.yaml:
services:
jobOrchestrator:
settings:
# Maximum jobs deployed in a single batch
batchSize: 20
# Job run cleanup configuration
jobRunCleanup:
enabled: true
# Retention period in seconds (default: 30 days)
retentionPeriod: 2592000
Settings Reference
| Setting | Default | Since | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
settings.batchSize | 20 | 3.15.0 | Maximum jobs validated and deployed per batch. |
settings.jobRunCleanup.enabled | true | 3.15.0 | Enable periodic cleanup of completed queue runs and logs. |
settings.jobRunCleanup.retentionPeriod | 2592000 | 3.15.0 | Retention period in seconds (30 days). Older runs are automatically deleted. |
System Properties
Configure queue behavior via Admin Portal → System Configuration:
| Property | Default | Since | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
job-orchestrator.queue.high.scheduling-share-percentage | 90 | 3.12.0 | Percentage of scheduling slots allocated to high-priority jobs. Remaining slots go to normal-priority jobs. |
job-orchestrator.queue.head-timeout-seconds | 3600 | 3.15.0 | Time (seconds) a job can remain blocked at queue head before timeout action. |
job-orchestrator.queue.head-retry-count | 0 | 3.15.0 | Number of retry attempts before cancelling a blocked job. Set to 0 for immediate cancellation after timeout. |
Advanced Features
Weighted Round Robin Scheduling [3.12.0+]
To prevent normal-priority job starvation, the orchestrator uses Weighted Round Robin (WRR) scheduling between priority queues.
Default behavior (90/10 split):
- 90% of scheduling slots go to high-priority jobs
- 10% go to normal-priority jobs
This ensures normal-priority jobs still progress even when the high-priority queue is busy.
Queue Head Blocking Prevention [3.15.0+]
Jobs blocked at the queue head due to quota limits are now automatically retried or cancelled after configurable thresholds. This prevents a single resource-intensive job from indefinitely blocking the entire queue.
How it works:
- When a job at queue head cannot be scheduled due to quota limits, the timeout counter starts.
- After
head-timeout-secondselapses, the system retries scheduling (ifhead-retry-count > 0). - After exhausting retries, the job is automatically cancelled with a clear reason.
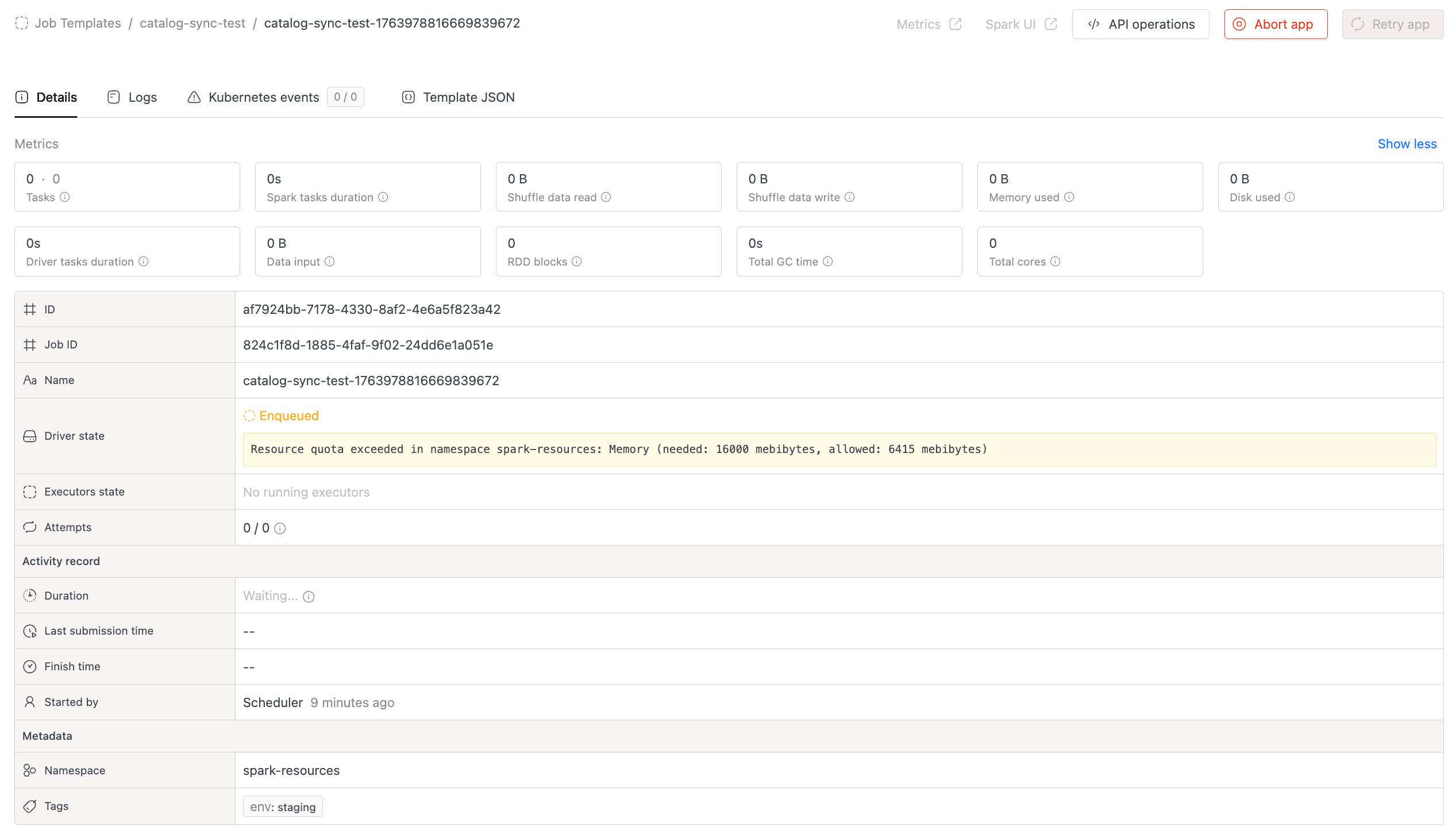
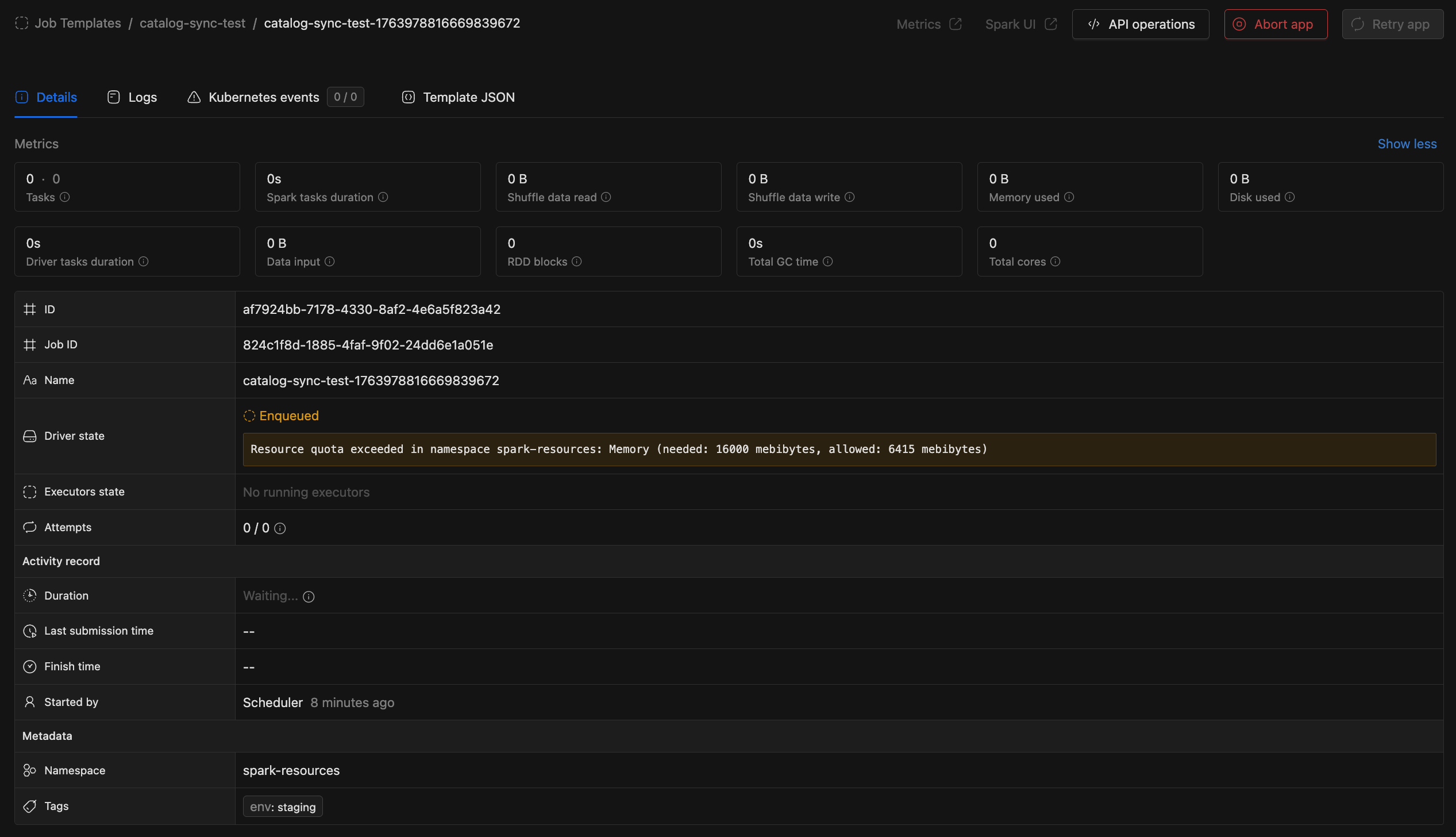
Job Queue Visibility [3.15.0+]
Job details now show the specific resource blocking deployment when a job is waiting in the queue:
- CPU - Insufficient CPU quota
- Memory - Insufficient memory quota
- Pods - Pod count limit reached
- Storage - Storage quota exceeded
The UI also displays queue timeout retries, cancellation reasons, and reschedule events.
Scheduling Reliability [3.15.0+]
Jobs incorrectly scheduled due to stale quota data are now automatically retried. This reduces failures caused by timing mismatches between quota checks and actual resource allocation.
Cleanup & Maintenance [3.15.0+]
The orchestrator automatically cleans up completed queue runs and logs to prevent unbounded data growth. Configure retention via jobRunCleanup settings in Helm values.
Monitoring
Monitoring is enabled out-of-the-box with a complete observability stack:
Components:
- Metrics Exporter - Deployed alongside the orchestrator to collect performance data.
- Prometheus Integration - Scrapes metrics for storage and alerting.
- Grafana Dashboards - Pre-built visualizations for job resources usage & run metrics.
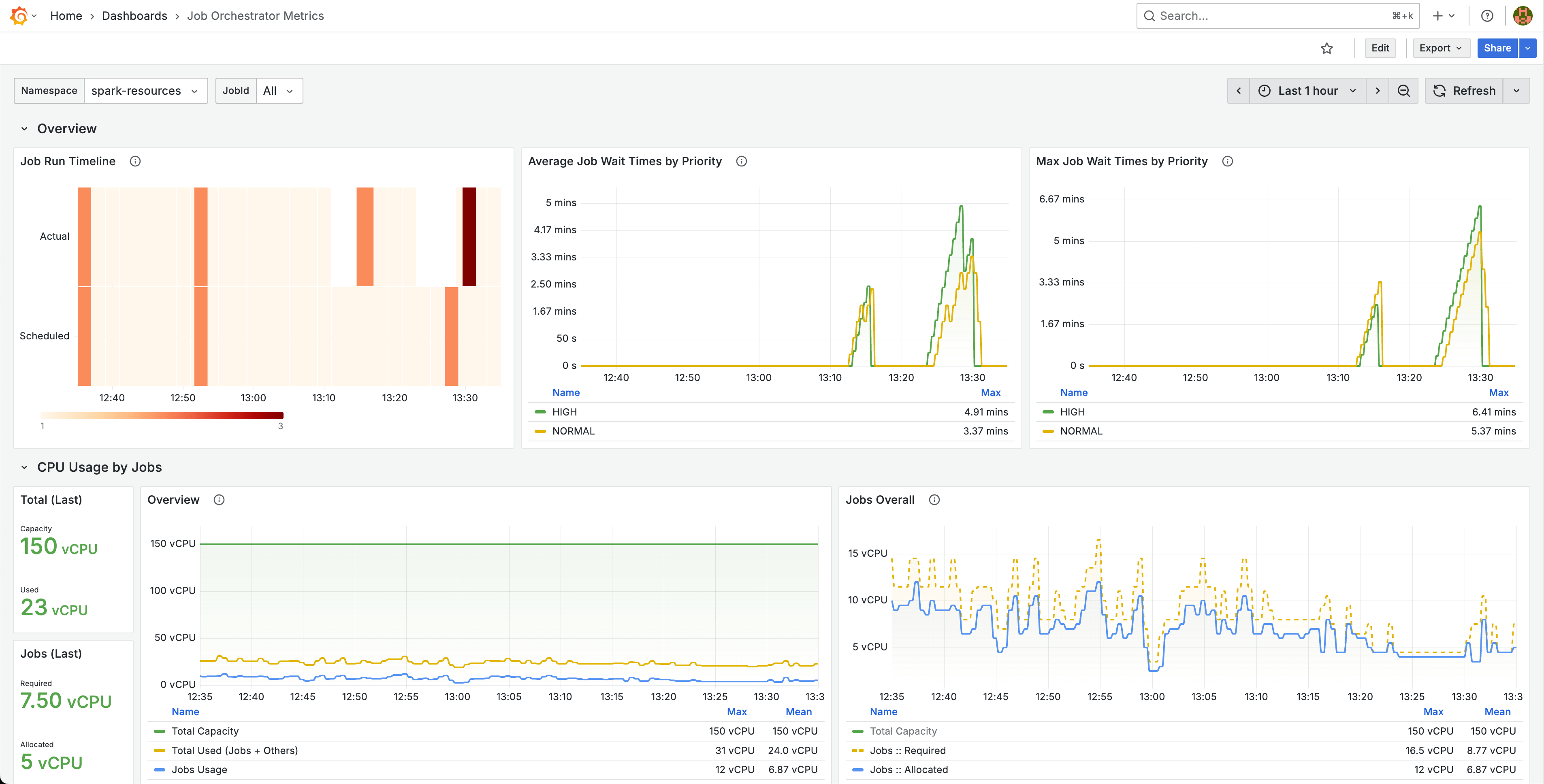
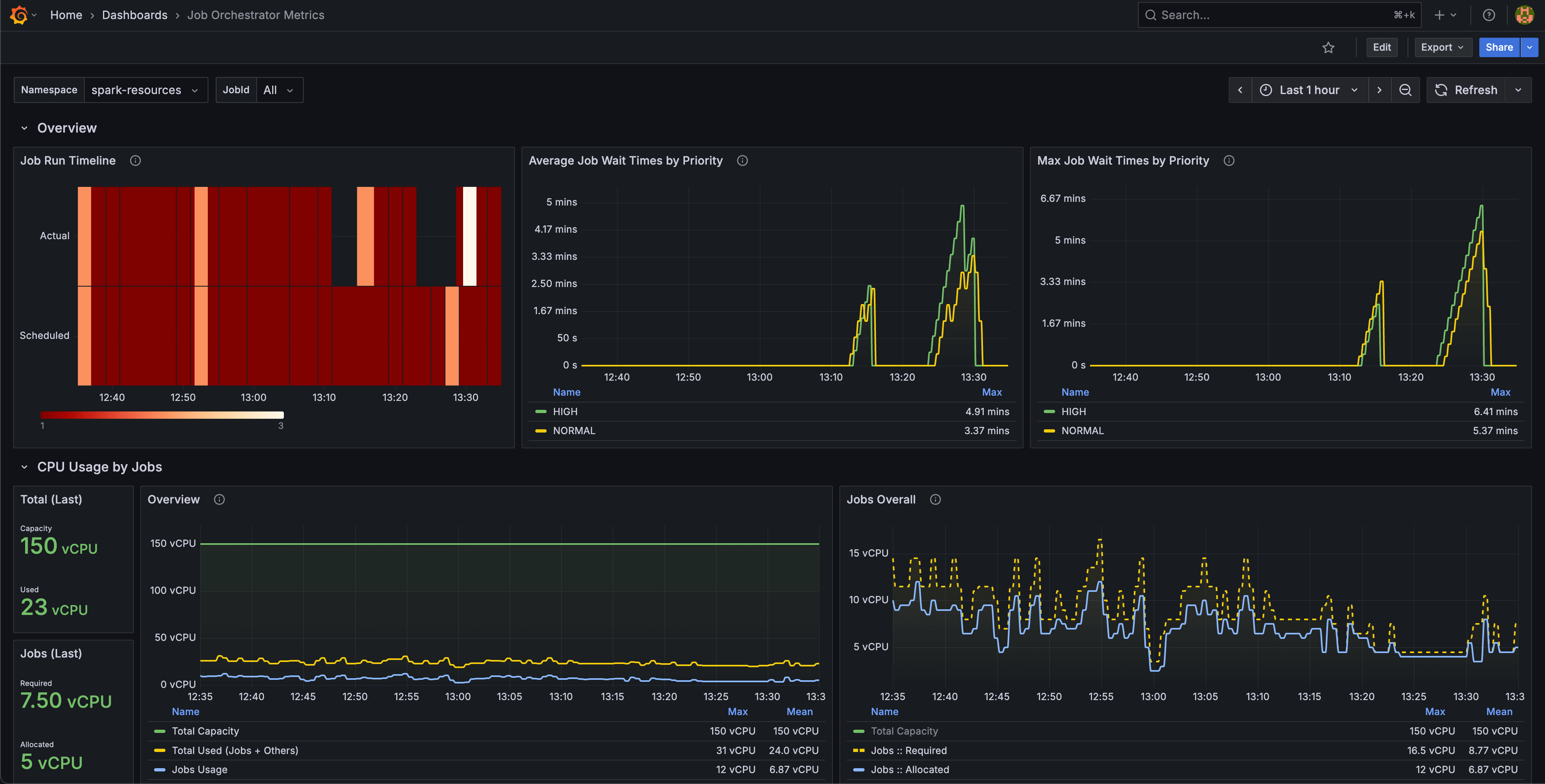
Custom Prometheus Setup
If you have your own Prometheus installation, add this scrape configuration:
# Job Orchestrator Metrics
- job_name: 'job-orchestrator-metrics'
scrape_interval: 30s
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
namespaces:
names:
- {{ .Release.Namespace }}
metrics_path: /metrics
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app]
regex: iom-job-orchestrator-metrics-exporter
action: keep
By default, metrics from the iom-job-orchestrator-metrics-exporter are exposed on port 8000.
How to Troubleshoot Common Issues
1. Job Orchestrator Won't Start - PostgreSQL Extension Error
Error Message:
sqlalchemy.exc.DBAPIError: (sqlalchemy.dialects.postgresql.asyncpg.Error)
<class 'asyncpg.exceptions.FeatureNotSupportedError'>: extension "pg_trgm"
is not allow-listed for users in Azure Database for PostgreSQL
HINT: to learn how to allow an extension or see the list of allowed extensions,
please refer to https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2301063
[SQL: CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_trgm;]
(Background on this error at: https://sqlalche.me/e/20/dbapi)
Cause: The Job Orchestrator uses the pg_trgm extension for partial string search functionality in the database.
Solution: Enable the extension in your PostgreSQL database: Allow extensions in Azure PostgreSQL
2. Jobs Stuck in Queue Due to Resource Constraints
Problem: Jobs remain queued even when cluster appears to have available resources.
Potential Causes:
- First job in queue requires more resources than currently available
- Resource fragmentation across different node types
- Quota limits blocking deployment
Automatic Handling (3.15.0+):
Starting from version 3.15.0, the orchestrator automatically handles blocked jobs:
- Jobs blocked at queue head are monitored via
head-timeout-seconds(default: 1 hour) - After timeout, the system retries based on
head-retry-countsetting - If retries are exhausted, the job is automatically cancelled with a clear reason
- The UI shows which resource (CPU, memory, pods, storage) is blocking deployment
Manual Solutions:
- Check the job details page to see which resource is blocking deployment
- Monitor cluster capacity through Grafana dashboards
- Adjust job resource requirements or scale cluster capacity
- Temporarily change problematic jobs to
Legacydeployment flow
3. All Jobs Stuck Due to One Problematic Job
With Queue Head Blocking Prevention enabled, this issue is now handled automatically. Jobs that cannot be scheduled are retried or cancelled after the configured timeout, preventing queue blockage.
Manual Fix (if needed):
- Navigate to the problematic job's configuration page
- Change the Deployment Flow from
Priority-BasedtoLegacy - This removes the job from the orchestrator queue and allows other jobs to proceed
- Debug the problematic job separately before re-enabling orchestration