Data Security
Data security at IOMETE maintains access control using a user interface for consistent administration. Security admins set policies for databases, tables, and columns, managing permissions for groups or users.
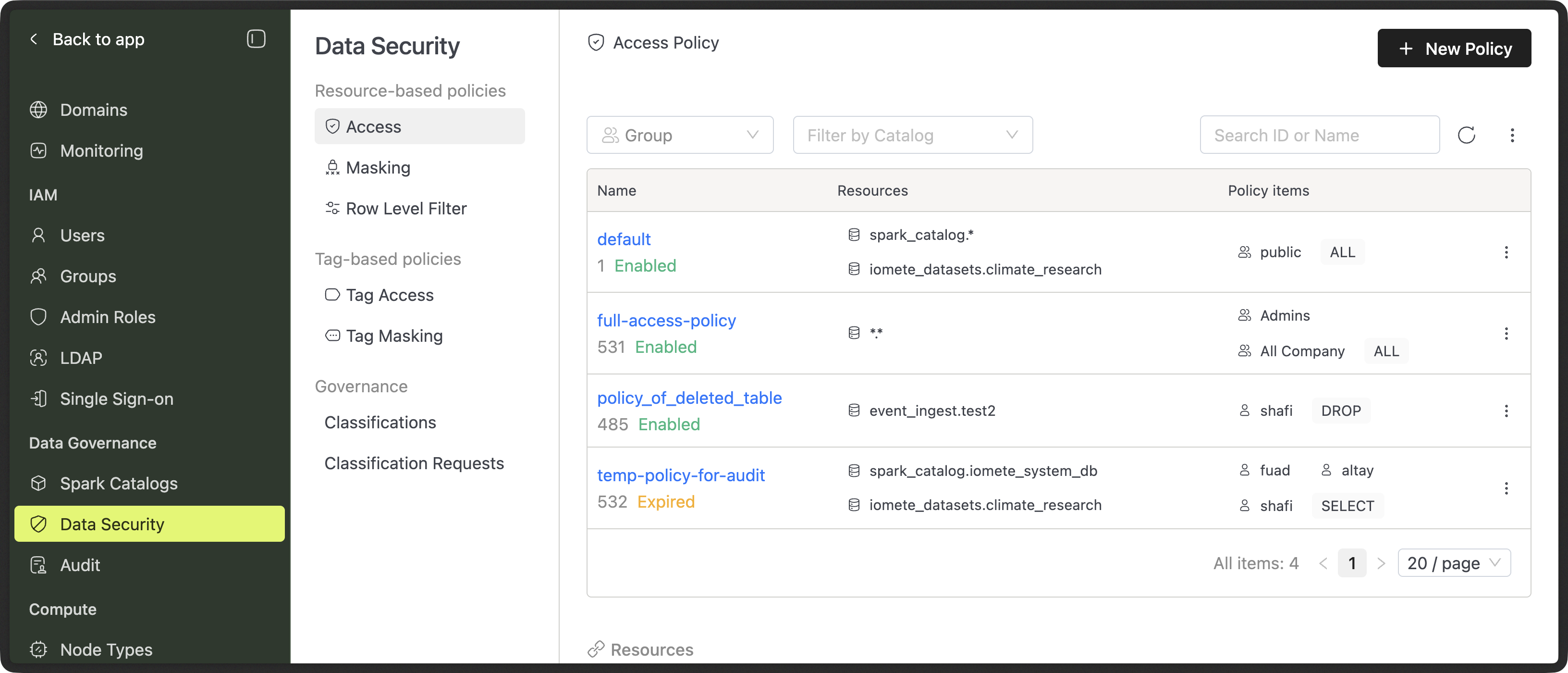

IOMETE has two types of policies: resource-based and tag-based.
Resource-based policies
Resource-based policies in IOMETE offers a powerful mechanism for enforcing security controls based on the resources being accessed. These policies cover three key areas:
| Policy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Policy | An access policy comprises rules and permissions that specify who can access specific resources and the actions they can take after gaining access. |
| Data Masking | Data masking is a method to hide sensitive information by changing it into fake data while keeping its appearance intact. It safeguards private details during testing or sharing. |
| Row-level Filter | Row-level filtering limits who can see certain rows in a database. |
Tag-based policies
Tag-based policies in IOMETE allow administrators to manage access controls to resources based on assigned tags. Instead of defining policies for individual resources, administrators group resources with similar characteristics under a common tag and apply access controls to the entire tag. This simplifies policy management and allows users or groups to access all resources sharing the same tag with consistent access permissions.
| Policy Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Tag-based Access Policy | Manage access controls to resources based on assigned tags. Resources with similar characteristics share common tags, and access controls are applied to the entire tag. |
| Tag-based Masking Policy | Control data masking within resources based on their assigned tags. Sensitive data is categorized with tags to indicate sensitivity levels. |
Data Classifications (Tags)
Data Classifications help you label tables and columns (for example: PII, Confidential, Financial). These labels are used by security and masking policies.
Because classifications directly affect data access and visibility, they now follow a request and approval workflow.
Key notes:
- Classifications must be predefined by admins or security teams
- Users without administrative priveledges cannot create new classifications
- Adding or removing a classification requires approval
- Every change is tracked through Classification Requests
This prevents accidental exposure of sensitive data and avoids breaking pipelines due to unexpected policy changes.