From JDBC Sources
This is an end-to-end guide about how to migrate tables from JDBC sources (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) to IOMETE and display it in the BI dashboard.
Intro
This is an end-to-end guide about how to migrate tables from JDBC sources (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) to iomete and display it in the BI dashboard.
First, you need to establish an SSH tunnel between iomete and your database in your private network.
Database to migrate
Let's assume that we want to replicate the MySQL database (or any other supported JDBC database) to the IOMETE warehouse
In this tutorial, we will be using a publicly accessible iomete-tutorial database instance that contains the Employees Sample Database.
Here are the details of iomete-tutorial public database:
Host: iomete-tutorial.cetmtjnompsh.eu-central-1.rds.amazonaws.com
Port: 3306
Username: tutorial_user
Password: 9tVDVEKp
The database contains the following tables:
| Table name | Row count |
|---|---|
| employees | 300024 |
| departments | 9 |
| dept_manager | 24 |
| dept_emp | 331603 |
| titles | 443308 |
| salaries | 2844047 |
Create warehouse
Create a new warehouse instance

Querying Source Table
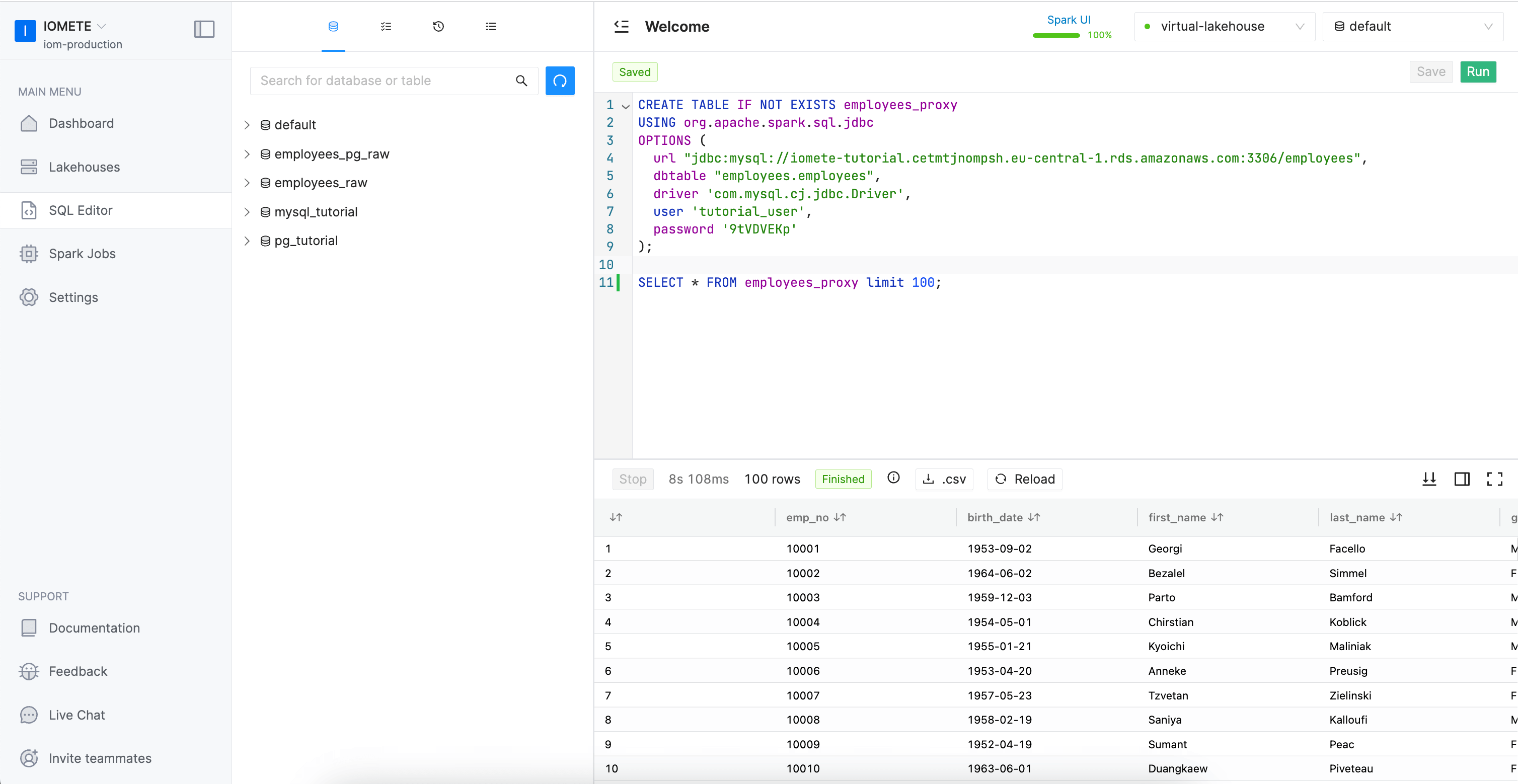
After having the lakehouse created, we create a table using JDBC Sources using CREATE TABLE command. In the OPTIONS part we specify credentials of the database to which we want to connect as follows
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employees_proxy
USING org.apache.spark.sql.jdbc
OPTIONS (
url "jdbc:mysql://iomete-tutorial.cetmtjnompsh.eu-central-1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306/employees",
dbtable "employees.employees",
driver 'com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver',
user 'tutorial_user',
password '9tVDVEKp'
);
SELECT * FROM employees_proxy limit 100;
This table doesn't hold the actual data. Data will be retrieved from the actual source once we query the table

Migrating Data
To move the data from the source to the warehouse, you can use one of the following options:
** Non-partitioned Table **
- Option 1. Create a table from select
-- Create table directly from the query
CREATE TABLE employees
AS SELECT * FROM employees_proxy;
-- To inspect the table use the following query
DESC TABLE EXTENDED employees;
- Option 2. Insert into to existing table
--just append data
INSERT INTO employees
SELECT * FROM employees_proxy
--or you can use the follwing command to overwerite data
--first clean an existing data and then insert new data
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE employees
SELECT * FROM employees_proxy
- Option 3. Merge with existing data
MERGE INTO employees
USING (SELECT * FROM employees_proxy) updates
ON employees.emp_no = updates.emp_no
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET *
WHEN NOT MATCHED
THEN INSERT *
Partitioning data to speed up queries or DML that have predicates involving the partition columns. Here let's create an artificial column birth_year from birth_date and partition data by birth_year
SELECT SUBSTRING(birth_date, 0, 4) as birth_year, * FROM employees_proxy LIMIT 100;
Partitioned Table
- Option 1. Create a partitioned table from select
-- Create a partitioned table directly from the query
CREATE TABLE employees_partitioned
PARTITIONED BY (birth_year)
AS SELECT SUBSTRING(birth_date, 0, 4) as birth_year, * FROM
employees_proxy order by birth_year;
-- To inspect the table use the following query
DESC TABLE EXTENDED employees_partitioned;
- Option 2. Insert into to existing table
--just append data
INSERT INTO employees_partitioned
SELECT SUBSTRING(birth_date, 0, 4) as birth_year, * FROM employees_proxy order by birth_year;
--or you can use the follwing command to overwerite data
--first clean an existing data and then insert new data
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE employees_partitioned
SELECT SUBSTRING(birth_date, 0, 4) as birth_year, * FROM employees_proxy order by birth_year;
- Option 3. Merge with existing data
MERGE INTO employees_partitioned
USING (SELECT
SUBSTRING(birth_date, 0, 4) as birth_year, * FROM employees_proxy) updates
ON employees_partitioned.emp_no = updates.emp_no
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET *
WHEN NOT MATCHED
THEN INSERT *
Visualize Data - Integration to BI applications:
Congratulations 🎉🎉🎉