Compaction behavior - Copy on Write(COW) vs Merge on Read(MOR)
Introduction
In today’s data-driven landscape, efficient data management is essential for organizations leveraging large-scale analytics. This document focuses on the behavior of table compaction operations for Copy-on-Write (COW) and Merge-on-Read (MOR) tables.
Table compaction plays a vital role in optimizing performance by consolidating smaller data files into larger ones, which reduces overhead and enhances query efficiency. This guide will walk you through the setup of catalogs and tables, data loading, updates, and the analysis of snapshots, providing a clear understanding of the compaction process within Iceberg and its benefits for effective data management.
Setup
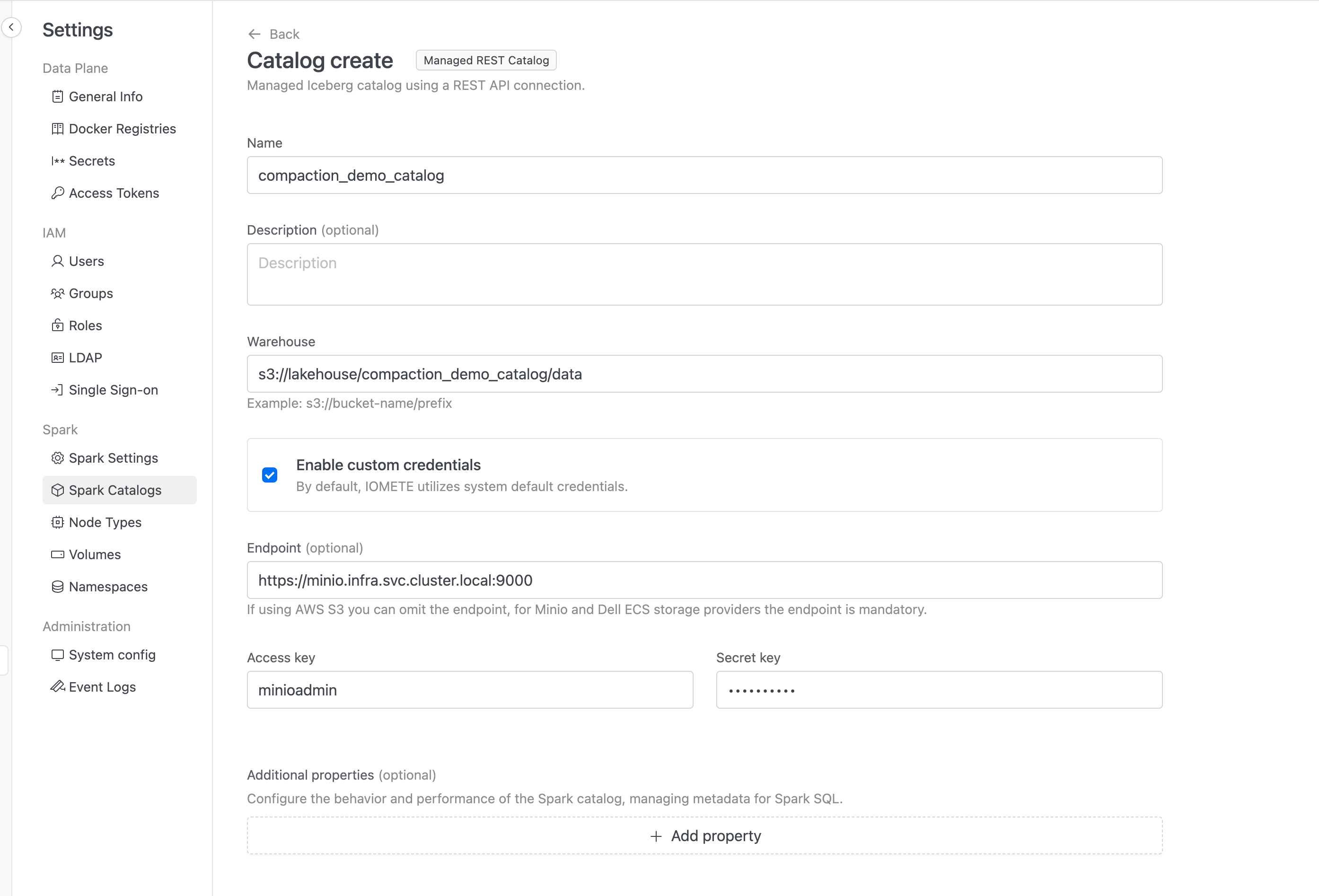
Create a catalog
Create database and tables
create database db_compaction;
CREATE TABLE db_compaction.copy_on_write_table
(
id BIGINT,
name STRING,
age INT,
zipcode STRING,
timestamp TIMESTAMP
)
TBLPROPERTIES
( 'write.update.mode' = 'copy-on-write',
'write.merge.mode' = 'copy-on-write',
'write.delete.mode' = 'copy-on-write');
CREATE TABLE db_compaction.merge_on_read_table
(
id BIGINT,
name STRING,
age INT,
zipcode STRING,
timestamp TIMESTAMP
)
TBLPROPERTIES
( 'write.update.mode' = 'merge-on-read',
'write.merge.mode' = 'merge-on-read',
'write.delete.mode' = 'merge-on-read');
This action will create the specified location at the designated path.
Loading Data
Insert Data
INSERT INTO db_compaction.copy_on_write_table (id, name, age, zipcode, timestamp)
VALUES (1, 'Alice', 30, '111111', CAST('2023-10-10 10:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(2, 'Bob', 25, '111111', CAST('2023-10-11 11:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(3, 'Charlie', 35, '111111', CAST('2023-10-12 12:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(4, 'David', 28, '111111', CAST('2023-10-13 13:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(5, 'Eve', 32, '111111', CAST('2023-10-14 14:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(6, 'Frank', 40, '111111', CAST('2023-10-15 15:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(7, 'Grace', 22, '111111', CAST('2023-10-16 16:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(8, 'Hank', 45, '111111', CAST('2023-10-17 17:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(9, 'Ivy', 38, '111111', CAST('2023-10-18 18:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(10, 'Jack', 29, '111111', CAST('2023-10-19 19:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP));
INSERT INTO db_compaction.merge_on_read_table (id, name, age, zipcode, timestamp)
VALUES (1, 'Alice', 30, '111111', CAST('2023-10-10 10:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(2, 'Bob', 25, '111111', CAST('2023-10-11 11:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(3, 'Charlie', 35, '111111', CAST('2023-10-12 12:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(4, 'David', 28, '111111', CAST('2023-10-13 13:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(5, 'Eve', 32, '111111', CAST('2023-10-14 14:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(6, 'Frank', 40, '111111', CAST('2023-10-15 15:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(7, 'Grace', 22, '111111', CAST('2023-10-16 16:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(8, 'Hank', 45, '111111', CAST('2023-10-17 17:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(9, 'Ivy', 38, '111111', CAST('2023-10-18 18:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)),
(10, 'Jack', 29, '111111', CAST('2023-10-19 19:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP));
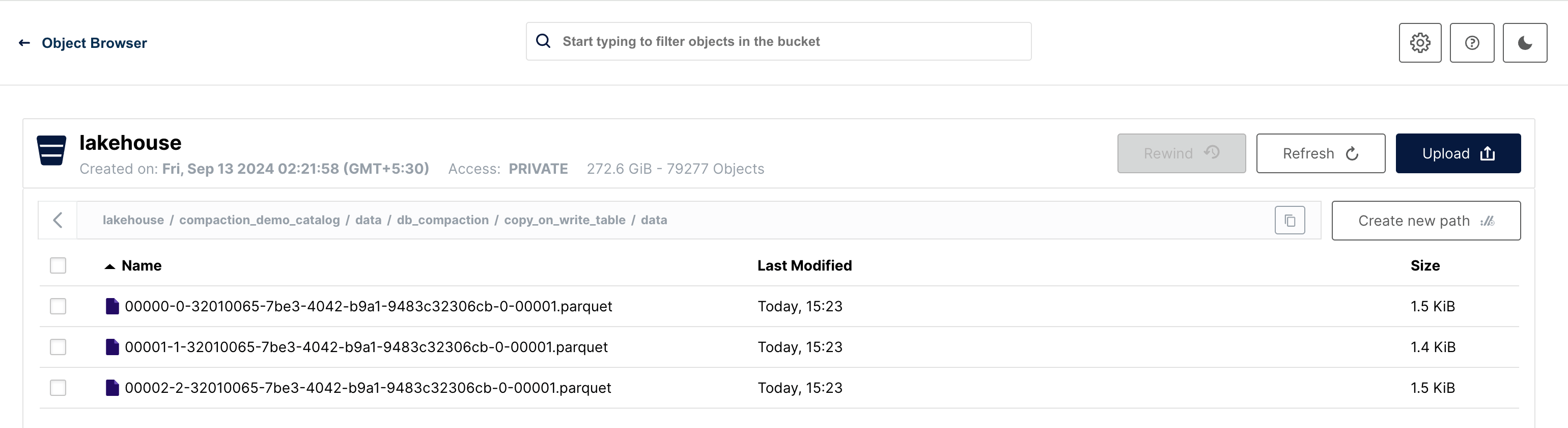
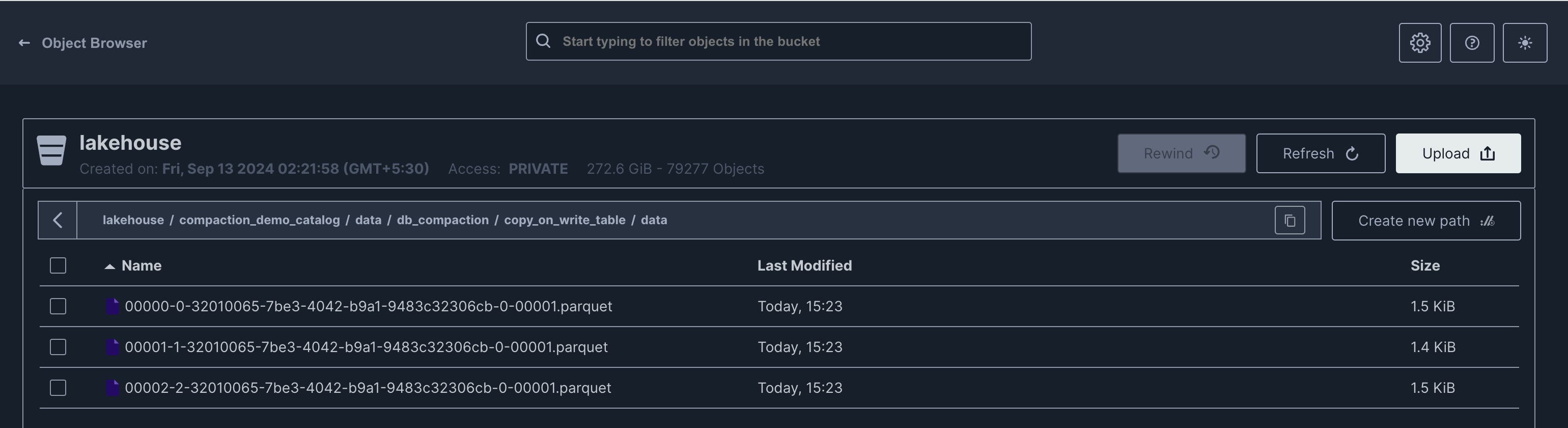
This will generate the data files in their designated locations.
Copy On Write (COW)
Merge On Read (MOR)
Update Data
UPDATE db_compaction.copy_on_write_table
SET age = age + 1
WHERE id IN (1, 2);
UPDATE db_compaction.merge_on_read_table
SET age = age + 1
WHERE id IN (1, 2);
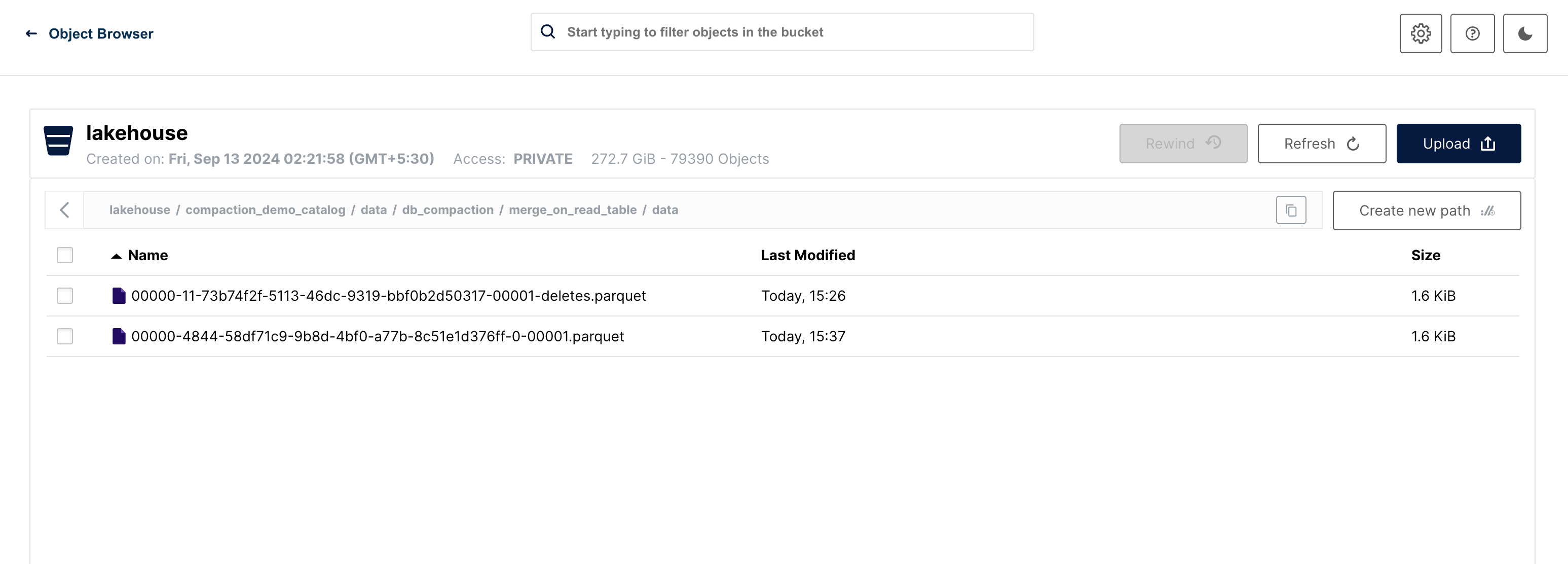
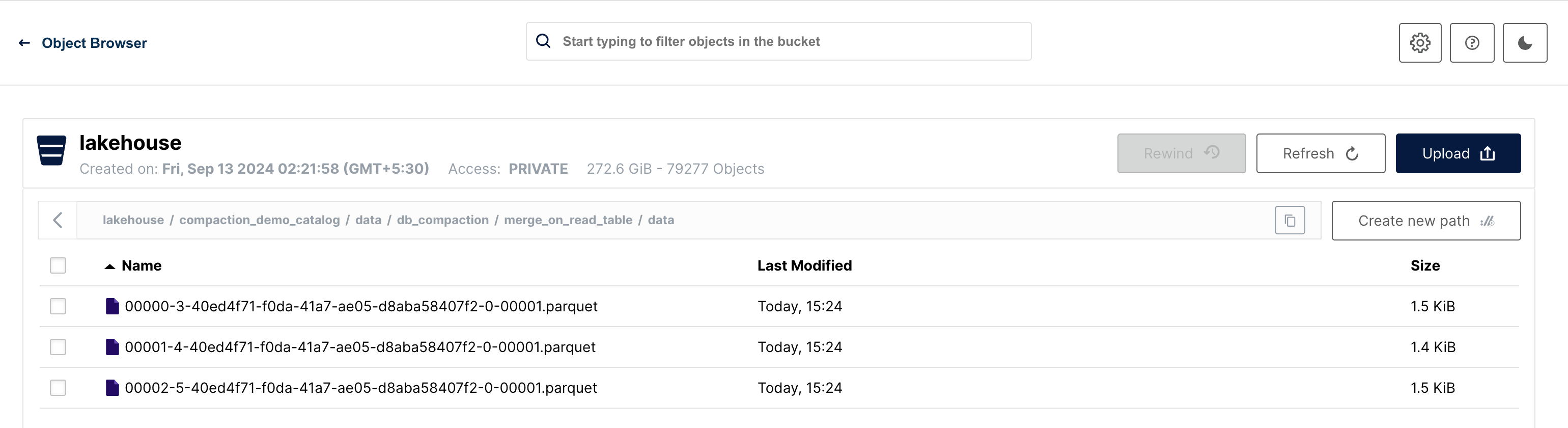
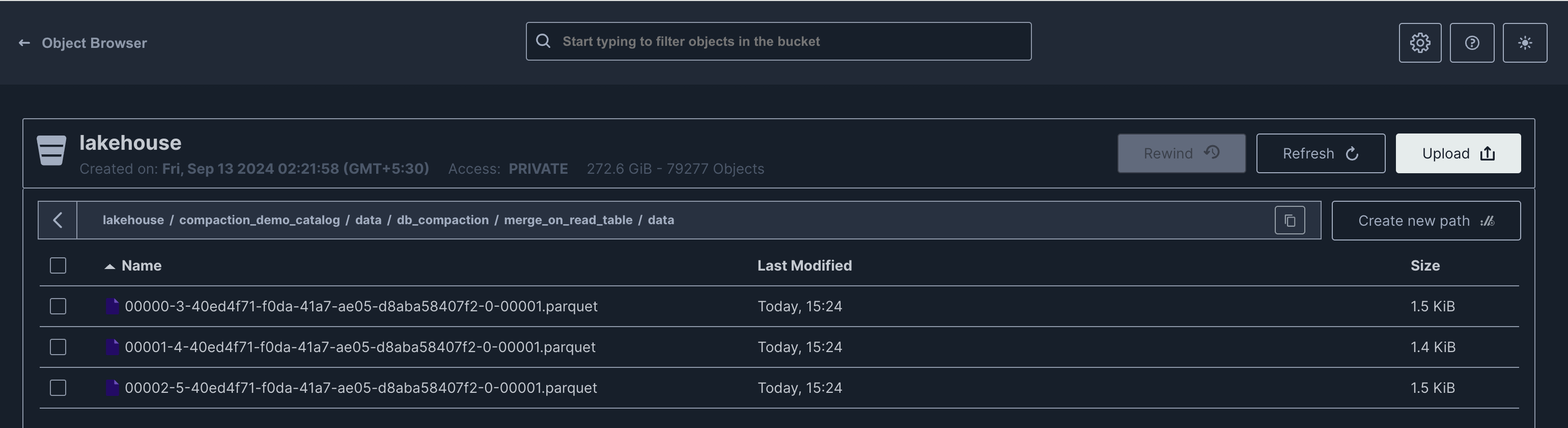
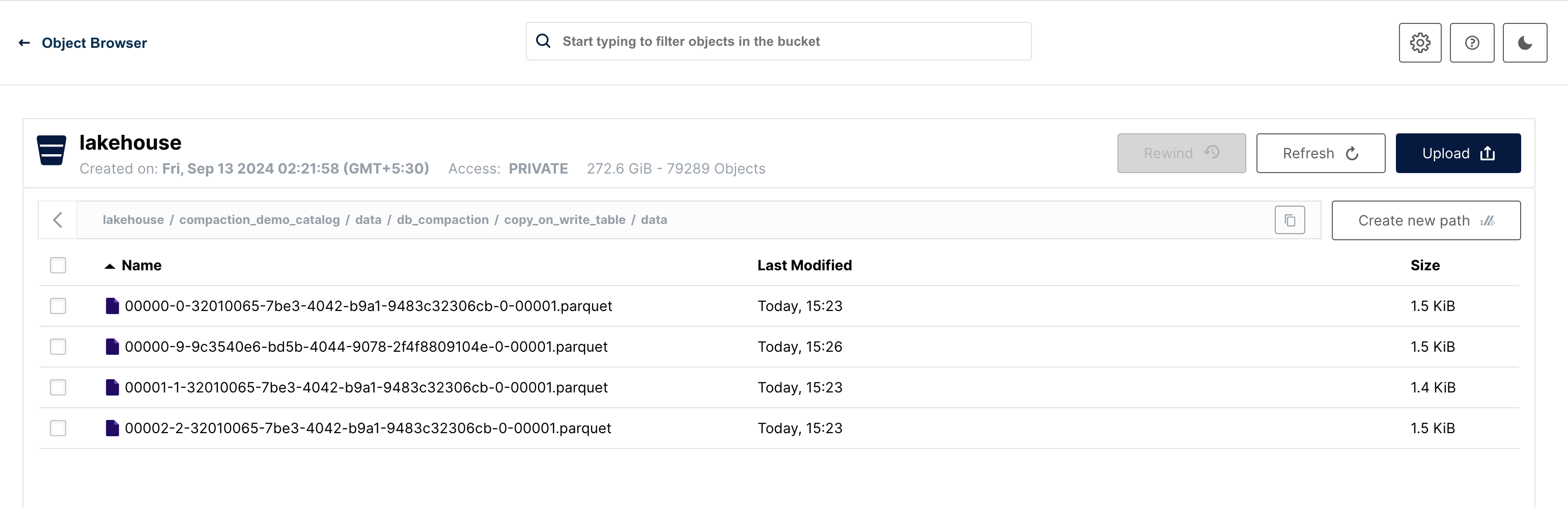
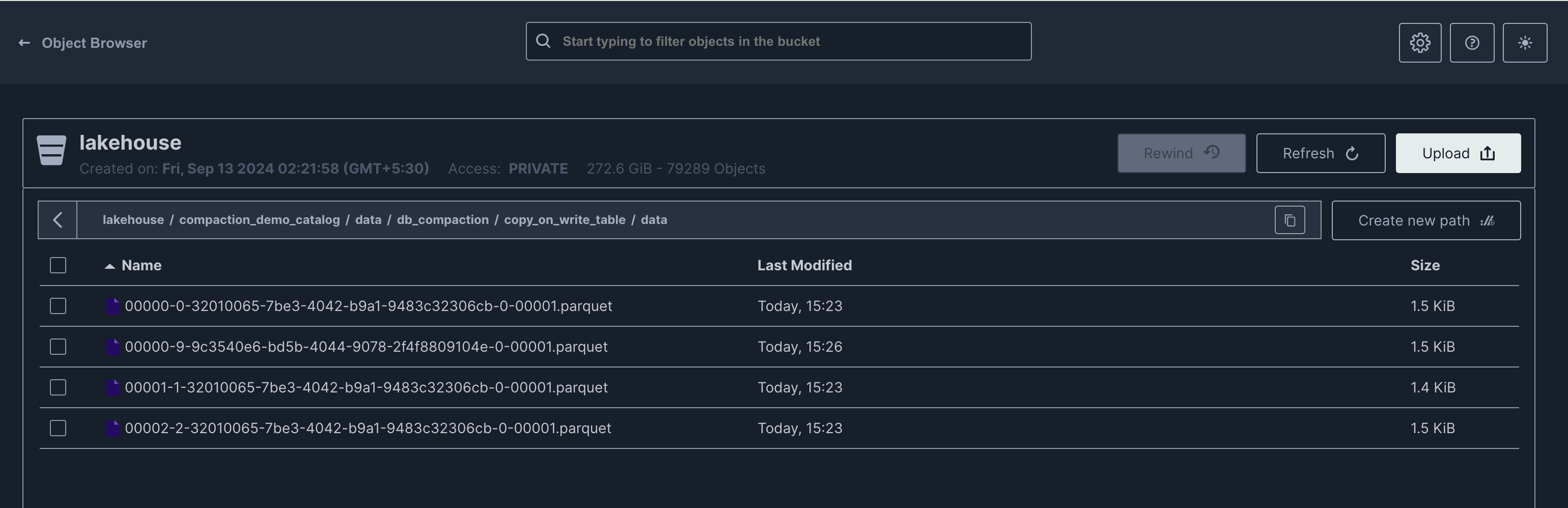
New files can be observed in the filesystem.
Copy On Write (COW)
Merge On Read (MOR)
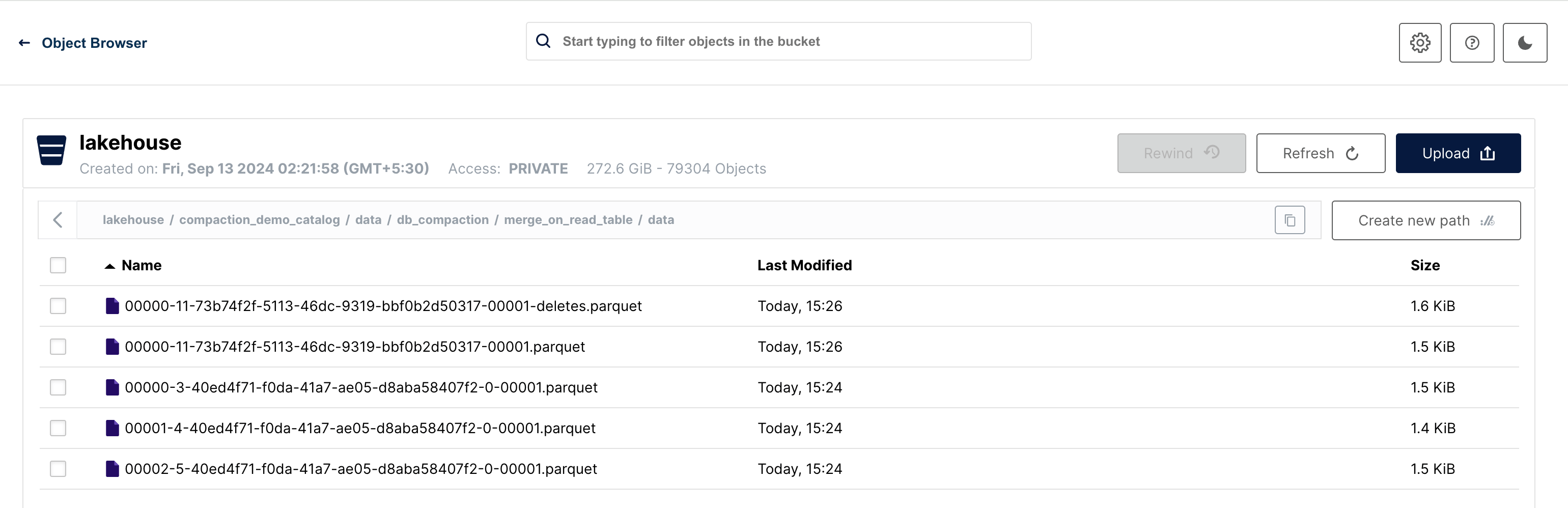
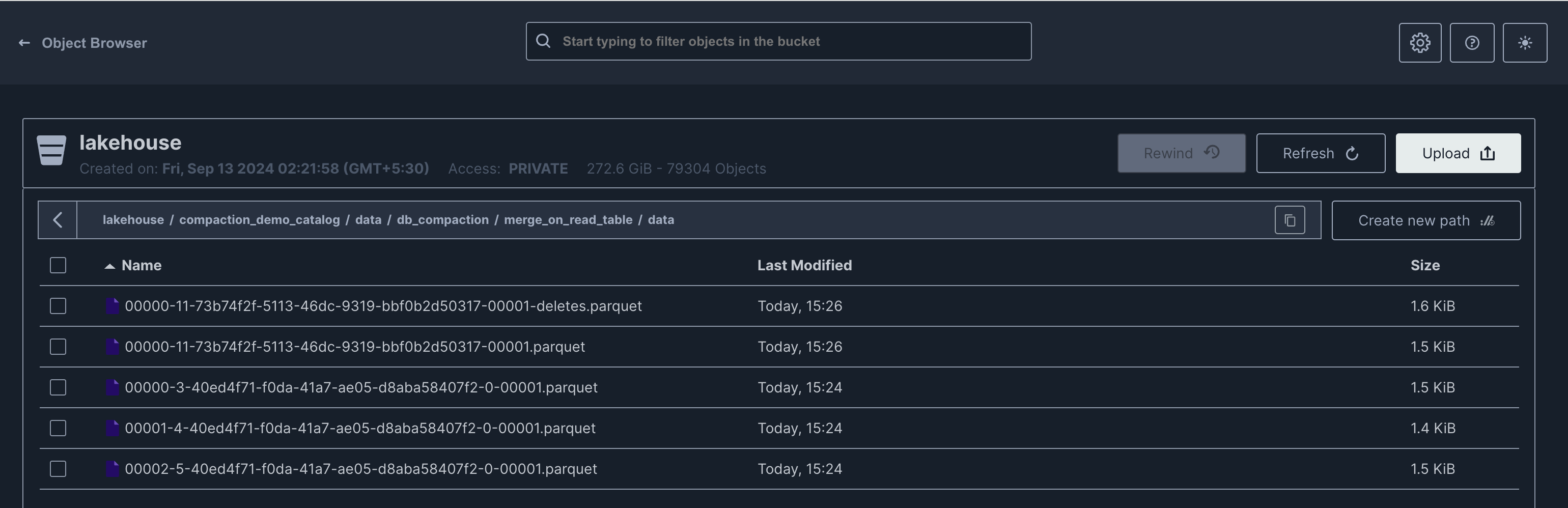
For Merge-on-Read (MOR), two new files are created: a delete file and a new data file.
Snapshots
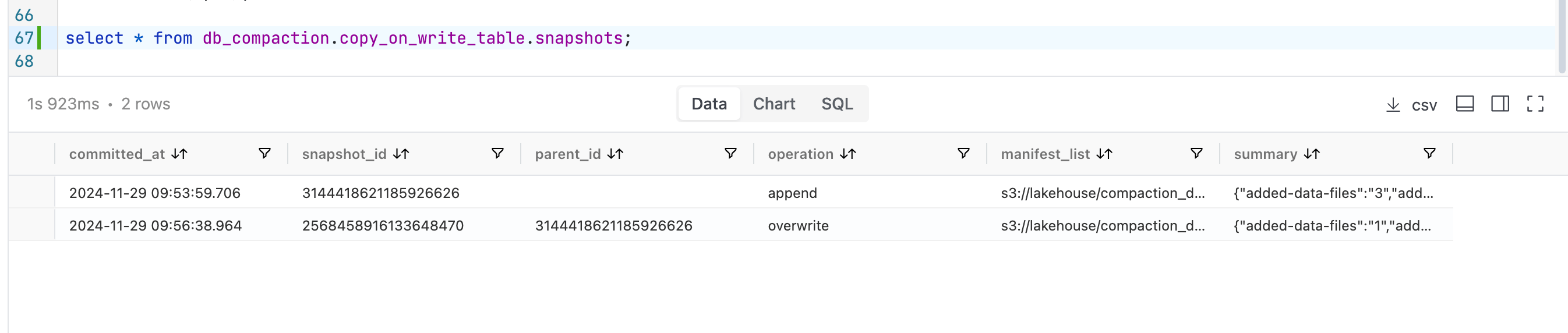
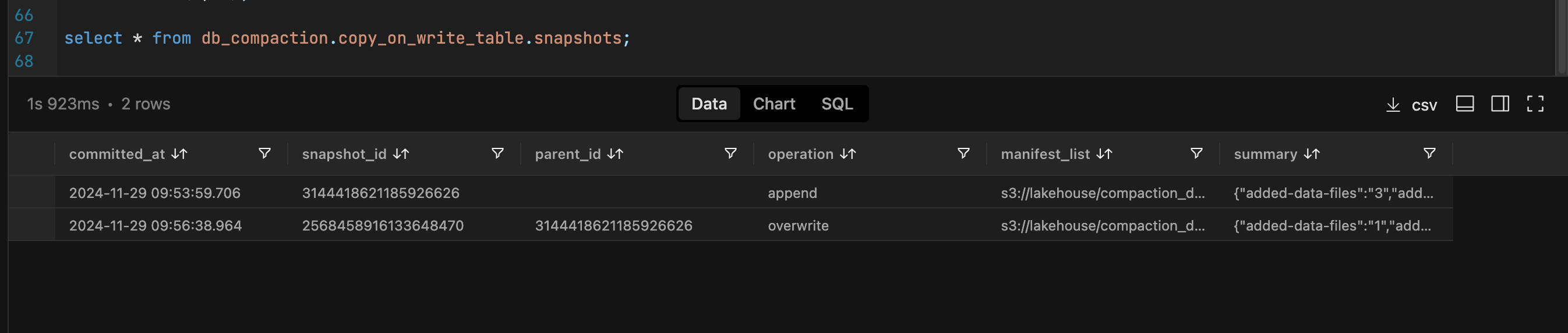
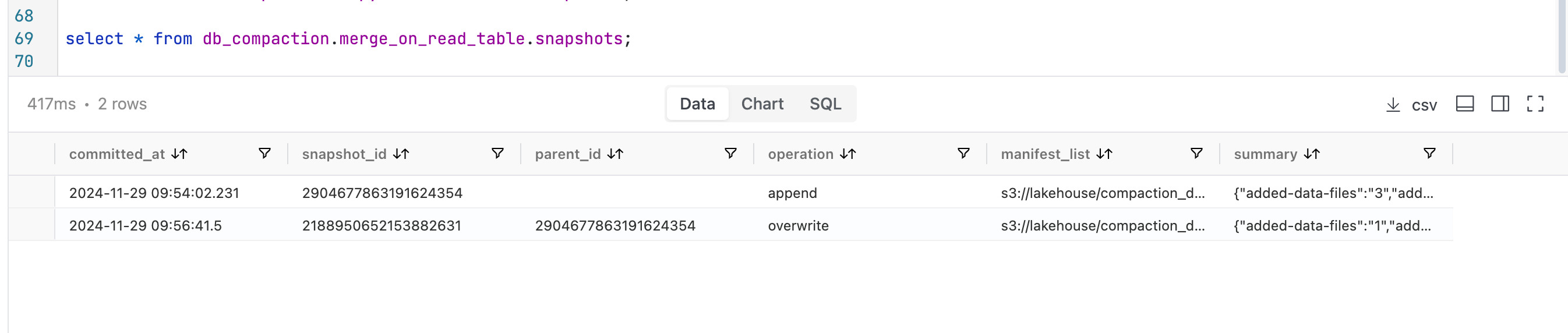
The image below illustrates that there are now two snapshots available for each of the tables.
Compaction Run 1
We can now perform compaction on this table, as we have two snapshots available.
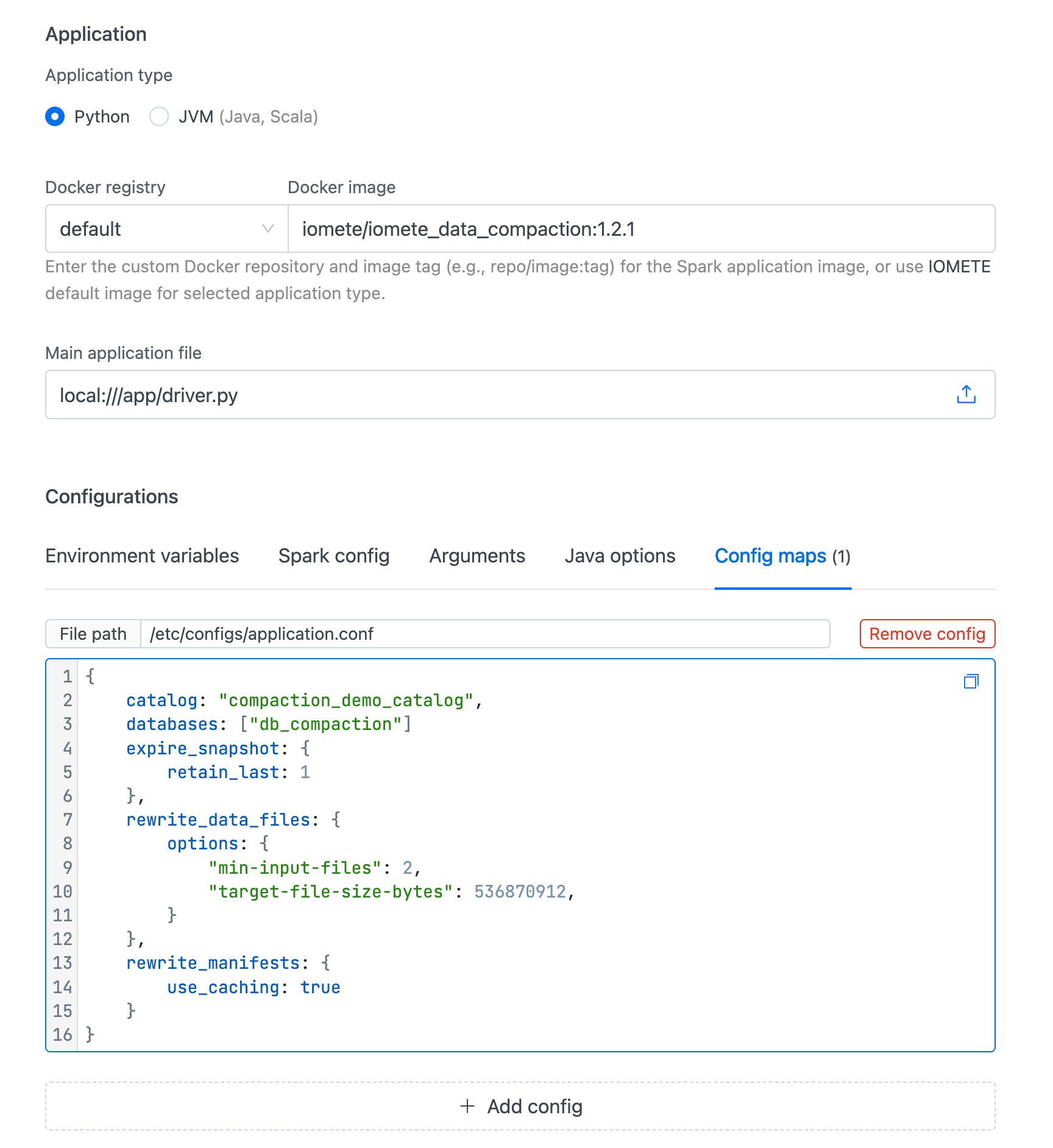
The system tables provide detailed insights into the actions taken during compaction.
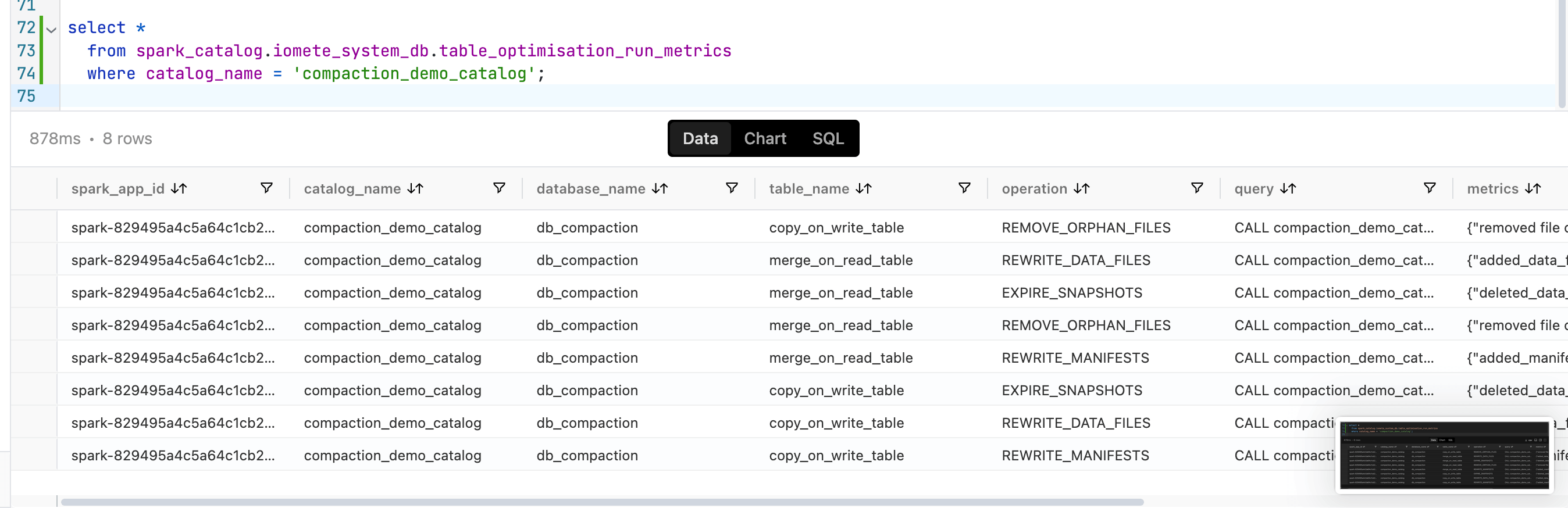
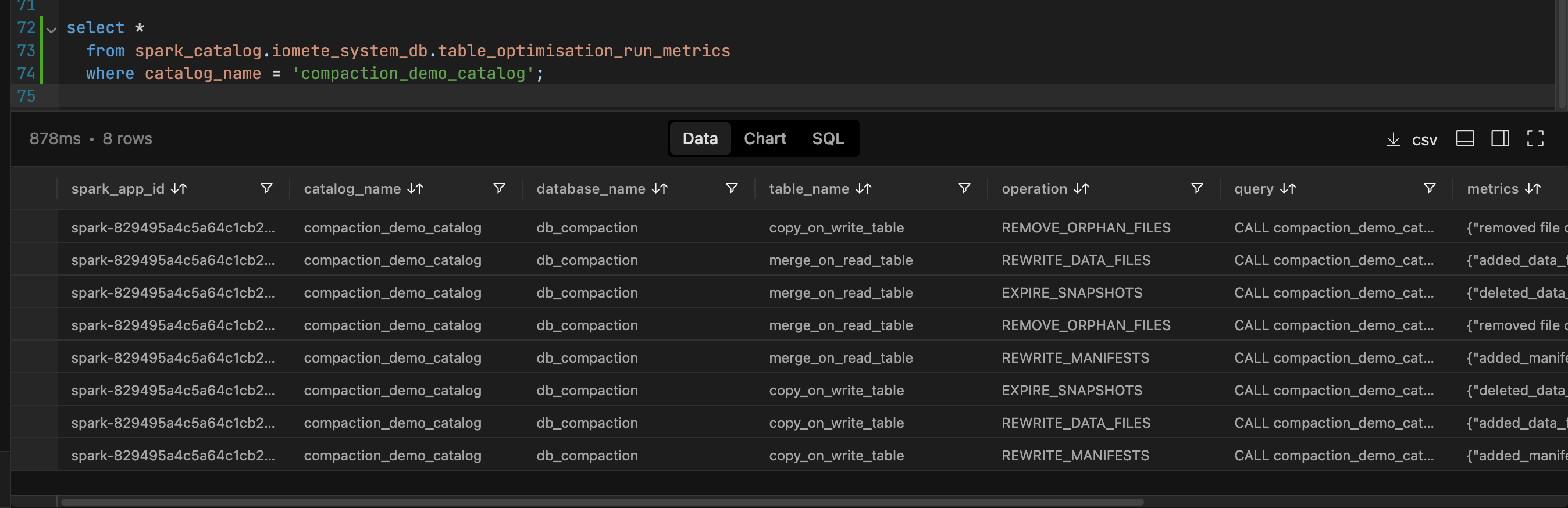
Snapshots
Examining the available snapshots now reveals the current state.
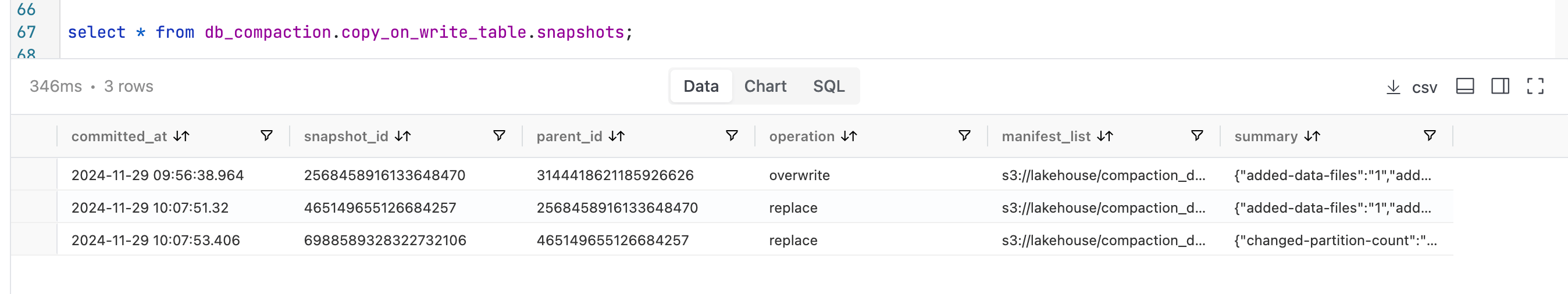
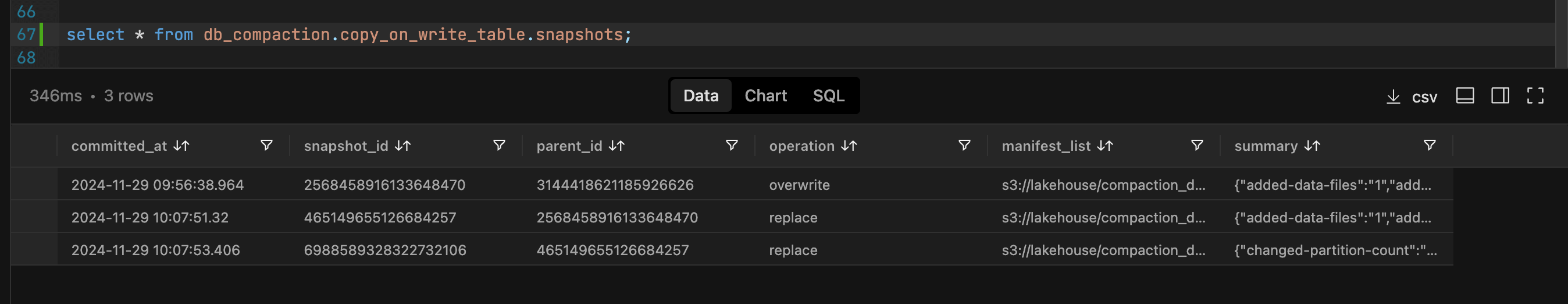
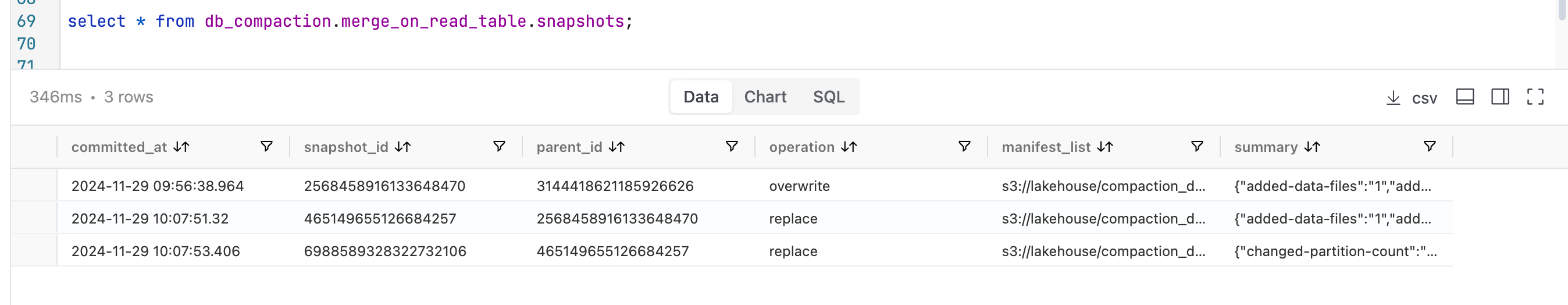
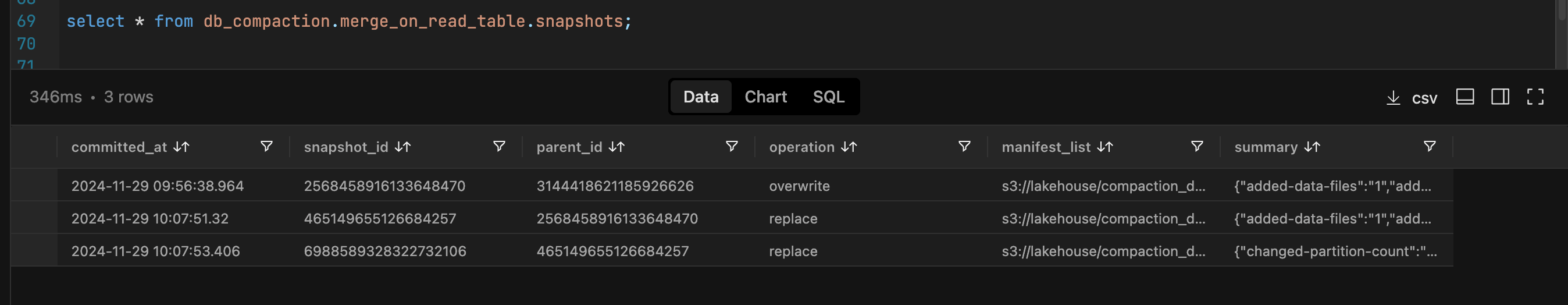
We can see that for both the tables there are now 3 snapshots available.
We began with two snapshots: the first for an insert operation and the second for an update. During the compaction process, the insert snapshot expires because we configured the system to retain only one snapshot during the expiration action.
The operation to rewrite data files generates a second snapshot, while the rewrite of manifest files results in a third snapshot. Consequently, we end up with a total of three snapshots.
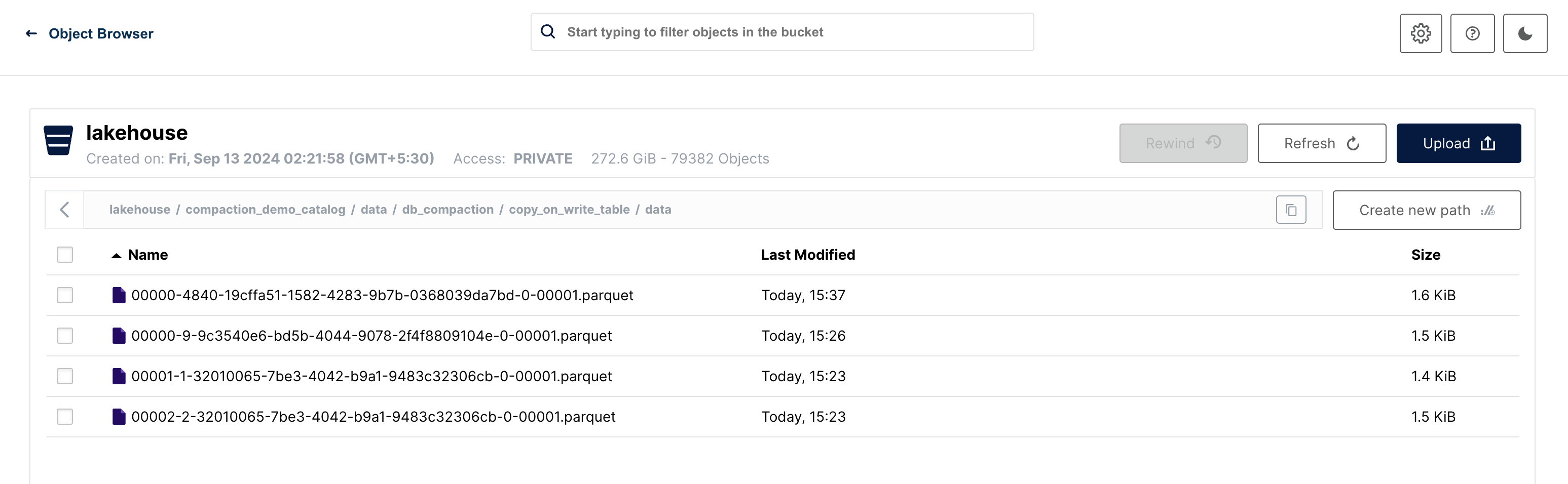
Datafiles
Copy On Write (COW)
There are currently four files remaining at the file system level. This situation arises from the existence of a snapshot of the update operation, which includes three of these files. The fourth file is the actual compacted file referenced by the latest snapshot. The older files will be eliminated during subsequent compaction runs as we now have newer snapshots available. This process will be illustrated in the following step.
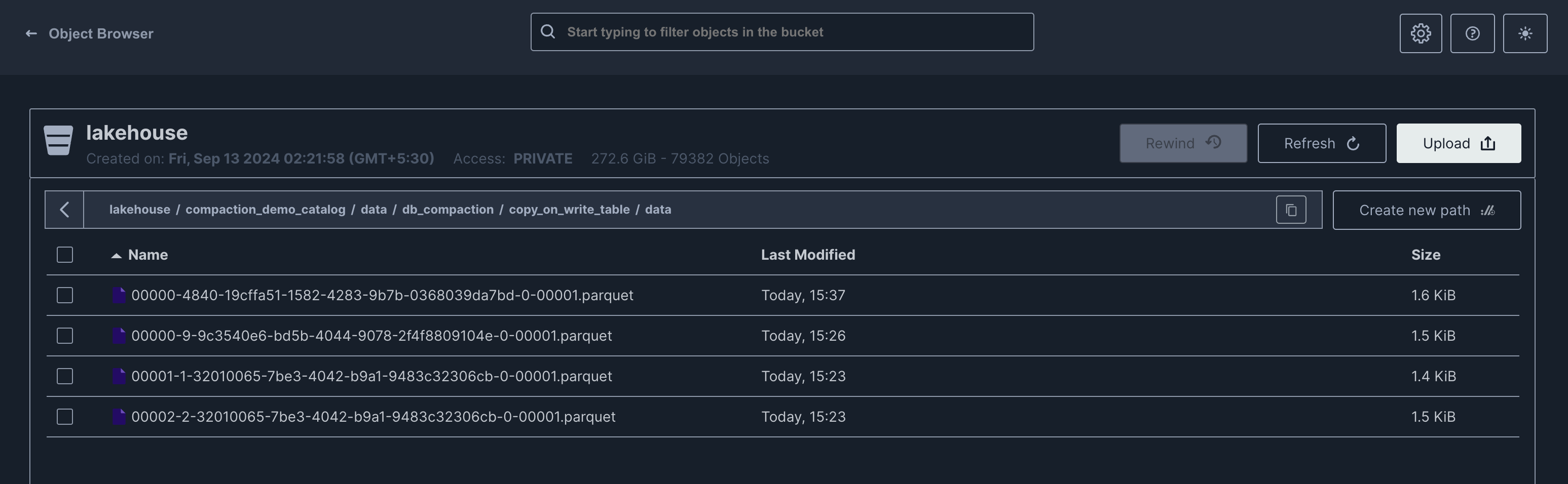
Merge On Read (MOR)
In a manner akin to COW, we maintain a single file that directs to the most recent snapshot; however, the majority of the files are linked to the earliest snapshot generated by the update command.
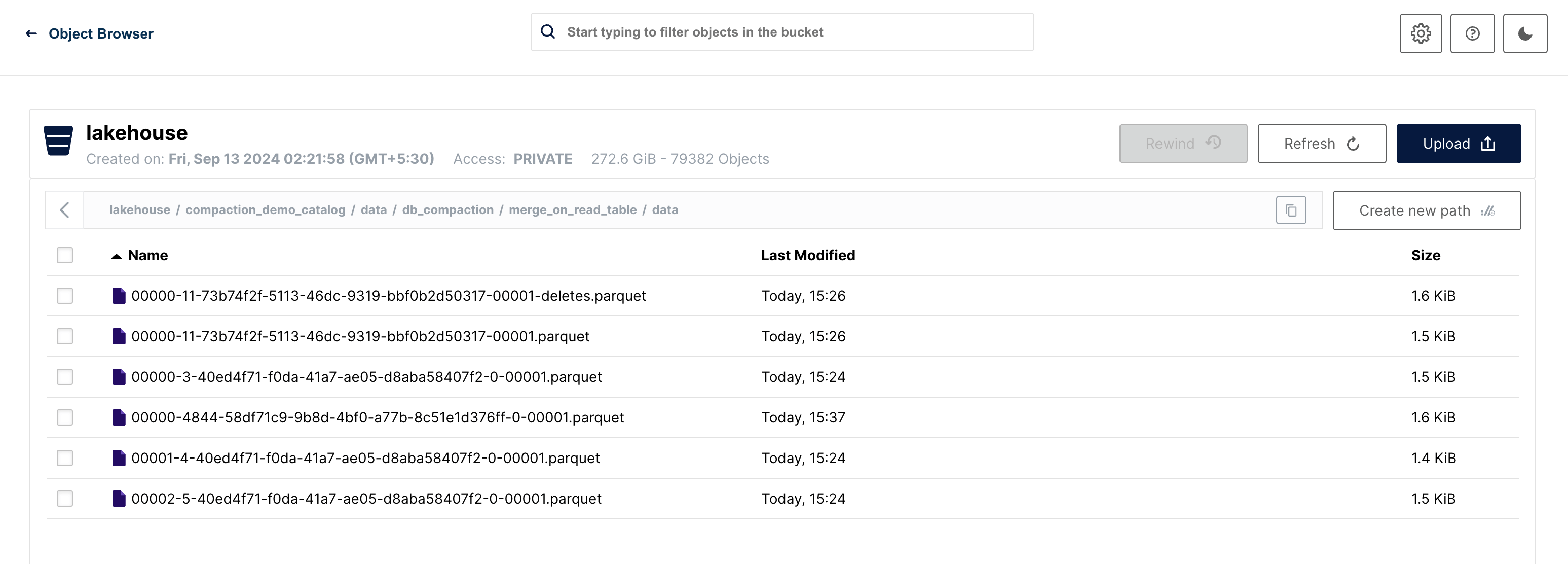
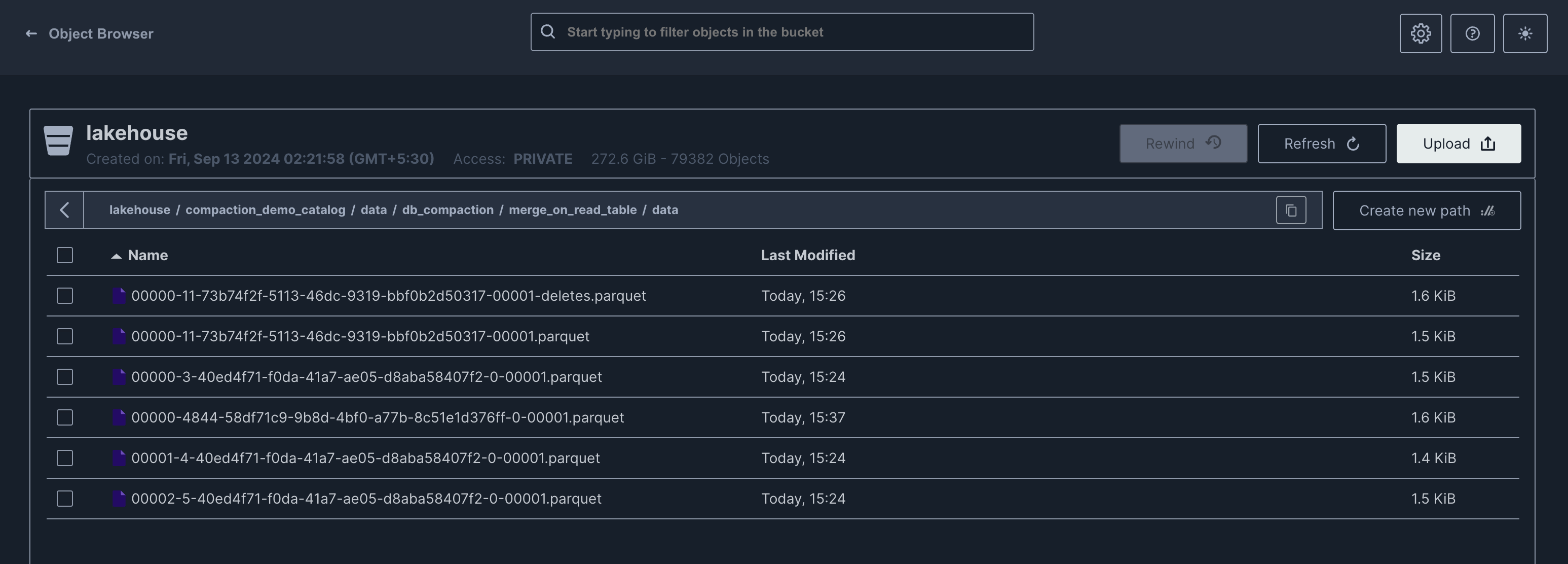
Compaction Run 2
Let us run compaction once again to depict the behavior in subsequent runs. This run now removes the update snapshot which had pointers to the older files that were still present, removing all those and the compacted file only remains
Copy On Write (COW)
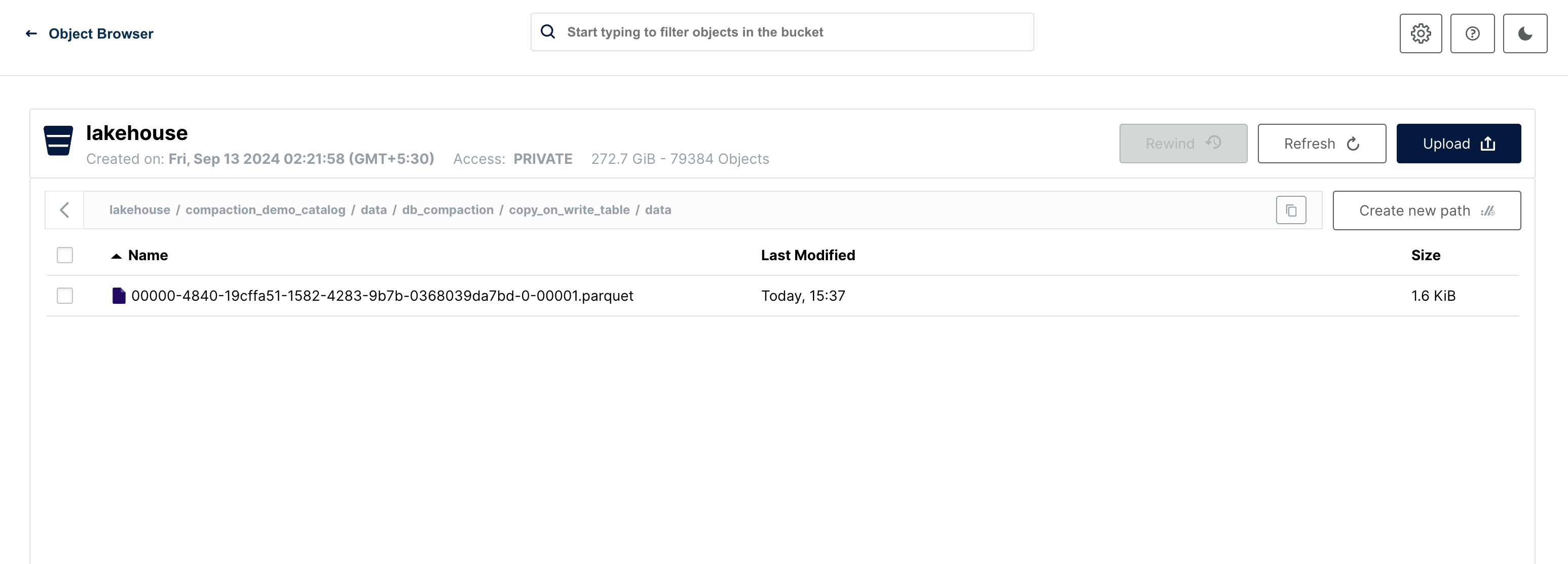
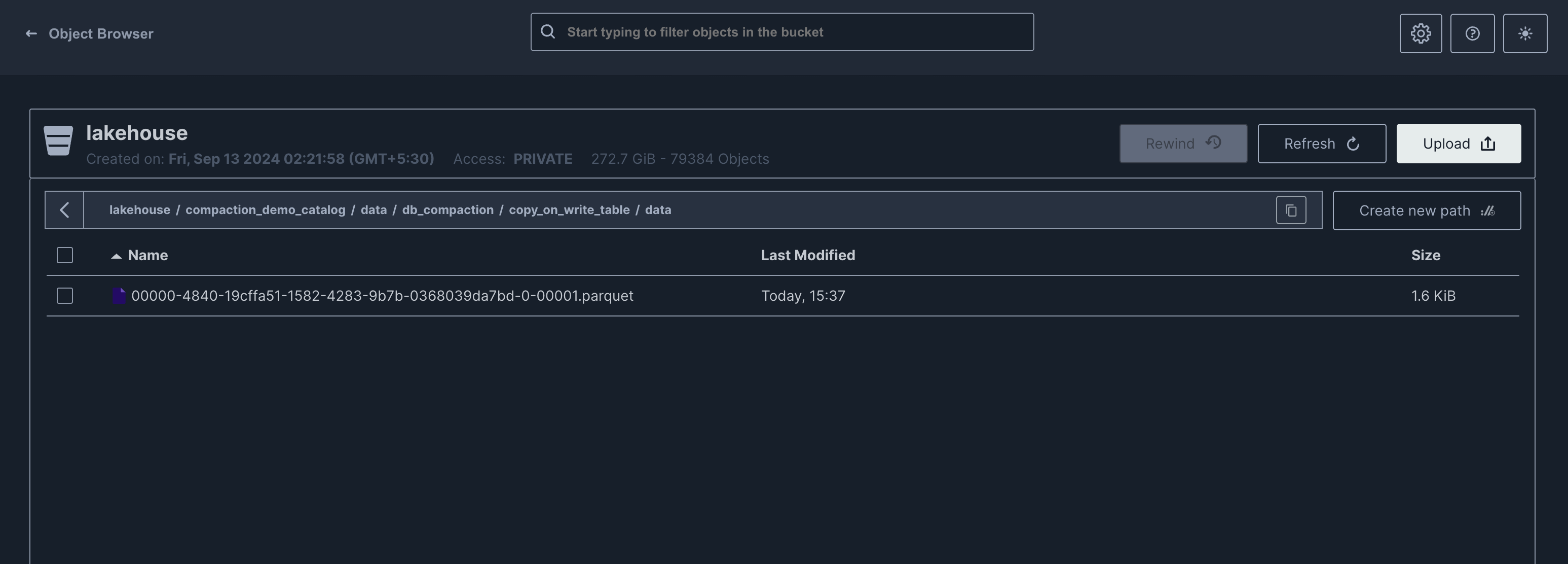
Merge On Read (MOR)