Storage Configs
Storage Configs in IOMETE allow you to configure and manage storage backends for your data infrastructure. These configurations define how IOMETE connects to external storage systems like S3-compatible storage providers, enabling secure and efficient data operations across your data platform.
Storage Config List
To view and manage your storage configurations, navigate to Settings → Storage Configs in the IOMETE console. This page displays all configured storage backends with their current status and key details.
Create, Edit, and Enable/Disable operations are only accessible to domain owners. Other users can consume and view the listing if they have access via the assigned resource bundles.
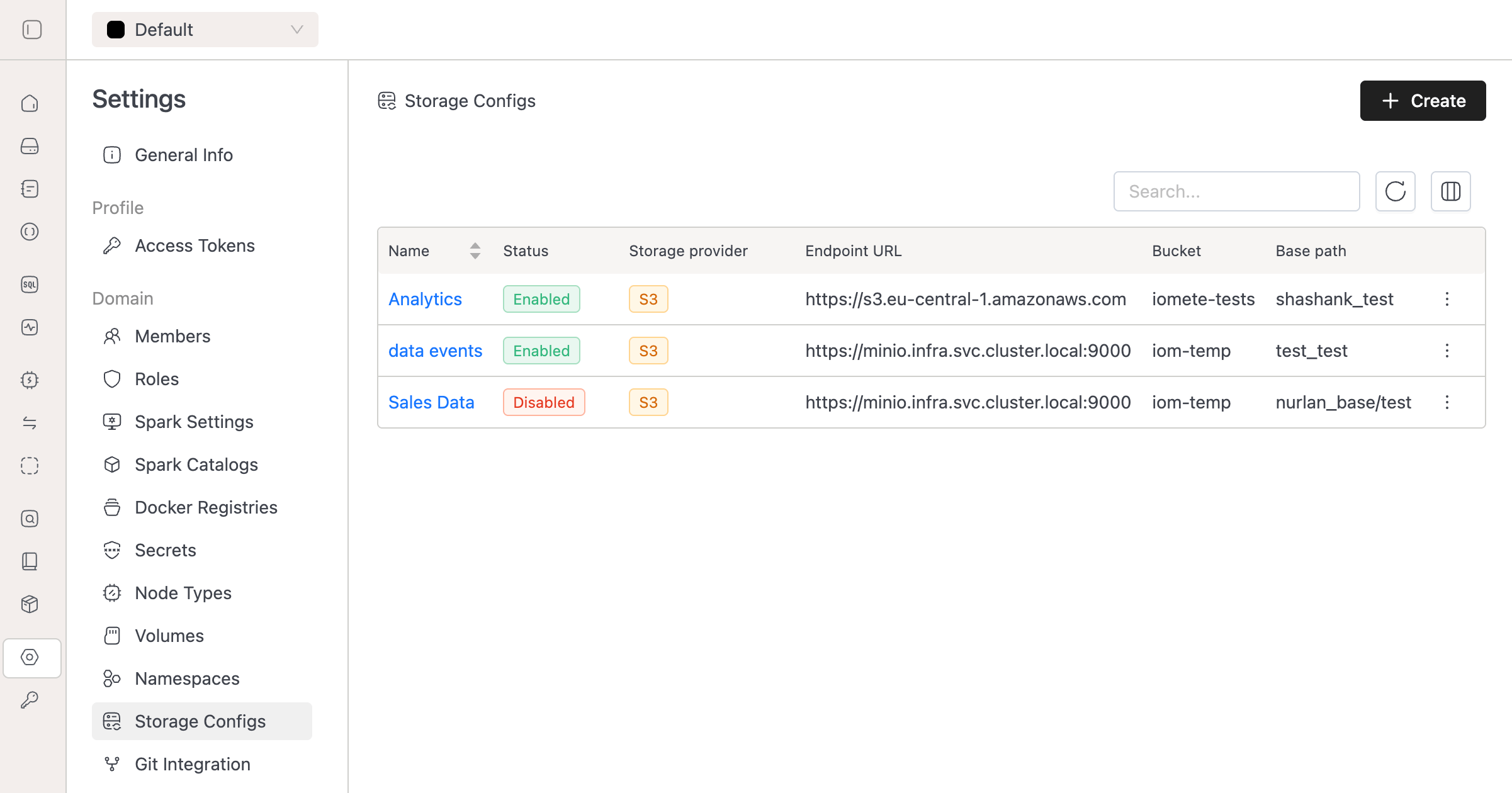
The storage configs list shows:
- Name: The identifier for your storage configuration.
- Status: Current connection status (Enabled/Disabled).
- Storage provider: The type of storage backend (e.g.,
S3). - Endpoint URL: The storage service endpoint.
- Bucket: The target storage bucket.
- Base path: The path prefix within the bucket.
Creating Storage Configs
To create a new storage configuration, click the Create button from the Storage Configs page. This opens the storage configuration form where you can define all necessary connection parameters.
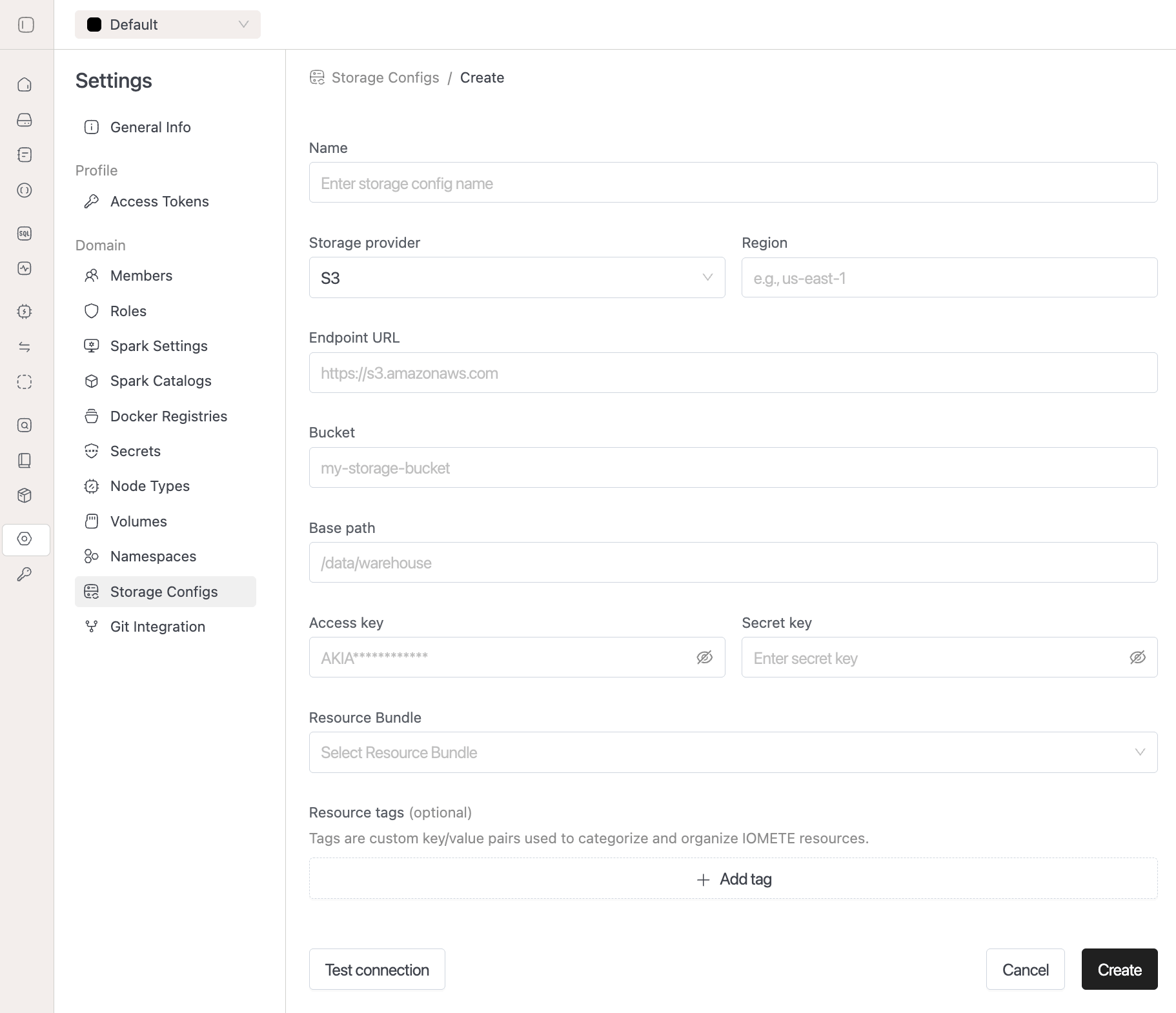
Configuration Fields
When creating a storage config, you'll need to provide the following information:
Basic Information:
- Name: A unique identifier for your storage configuration. Use descriptive names that reflect the purpose or environment (e.g.,
analytics,data-events,production-storage).
Storage Provider Details:
- Storage provider: Currently supports S3-compatible storage providers.
- Region: The geographic region where your storage bucket is located (e.g.,
us-east-1). - Endpoint URL: The storage service endpoint URL. For AWS S3, use
https://s3.amazonaws.comor region-specific endpoints. - Bucket: The name of the storage bucket where data will be stored.
- Base path: The path prefix within the bucket to organize data (e.g.,
/data/warehouse,/analytics/team_data).
Authentication:
- Access key: The access key ID for authentication with the storage provider.
- Secret key: The secret access key corresponding to the access key ID.
Advanced Configuration:
- Resource Bundle: Select the predefined resource bundles to manage the storage config accesses.
- Resource tags: Custom key-value pairs for resource organization and management. Click Add tag to include metadata tags for categorization.
The combination of Bucket + Base Path must be unique across all storage configurations, regardless of the Endpoint URL. This ensures data isolation and prevents conflicts between different storage configs.
Testing Connections
Before saving your storage configuration, use the Test connection feature to verify that IOMETE can successfully connect to your storage backend with the provided credentials.
Successful Connection
When your configuration is correct, you'll see a success message confirming the connection:
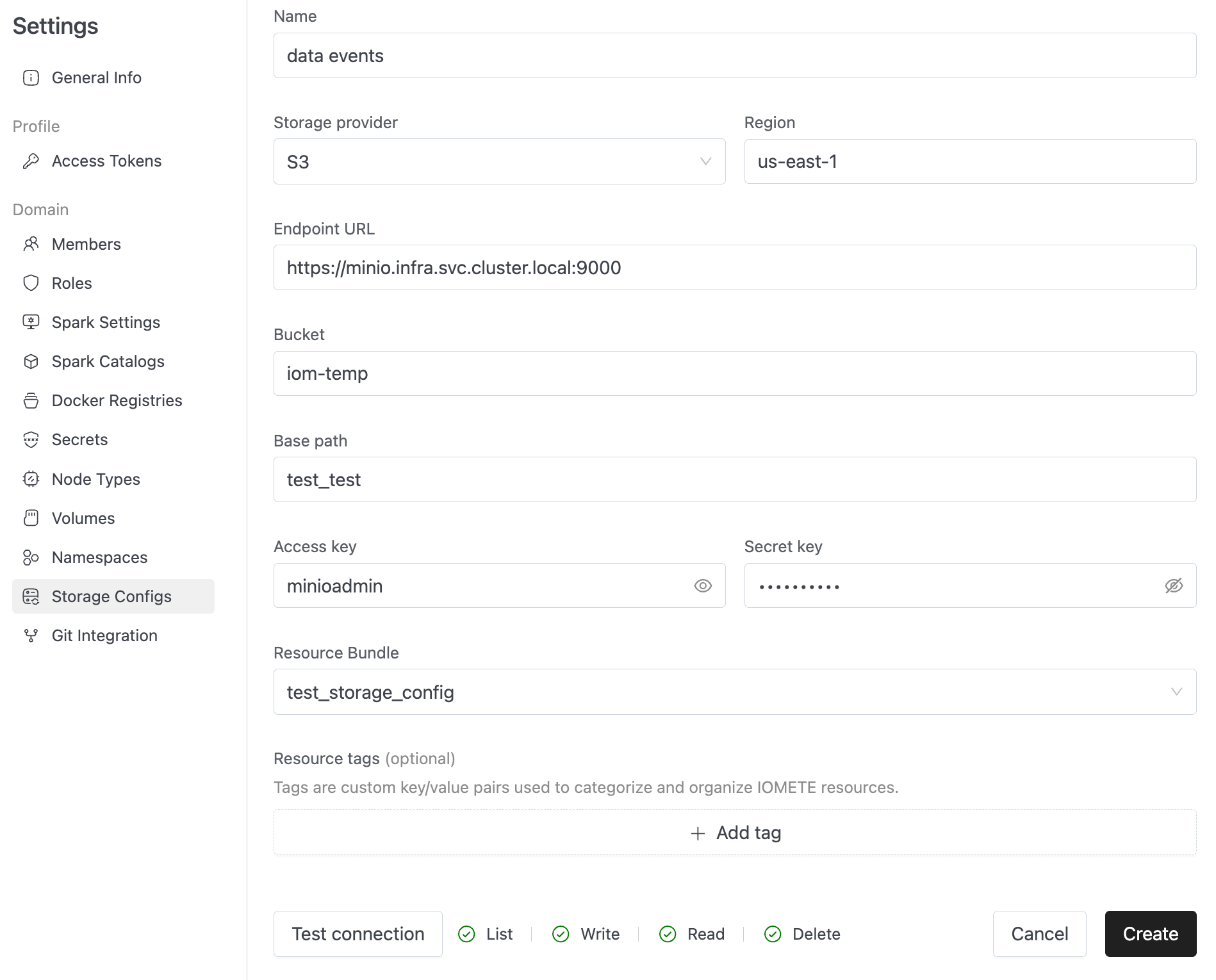
The test validates:
- Network connectivity to the endpoint.
- Authentication with provided credentials.
- Access permissions to the specified bucket.
- Ability to read and write data in the base path.
Failed Connection
If there are issues with your configuration, the test will show specific error details to help you troubleshoot:
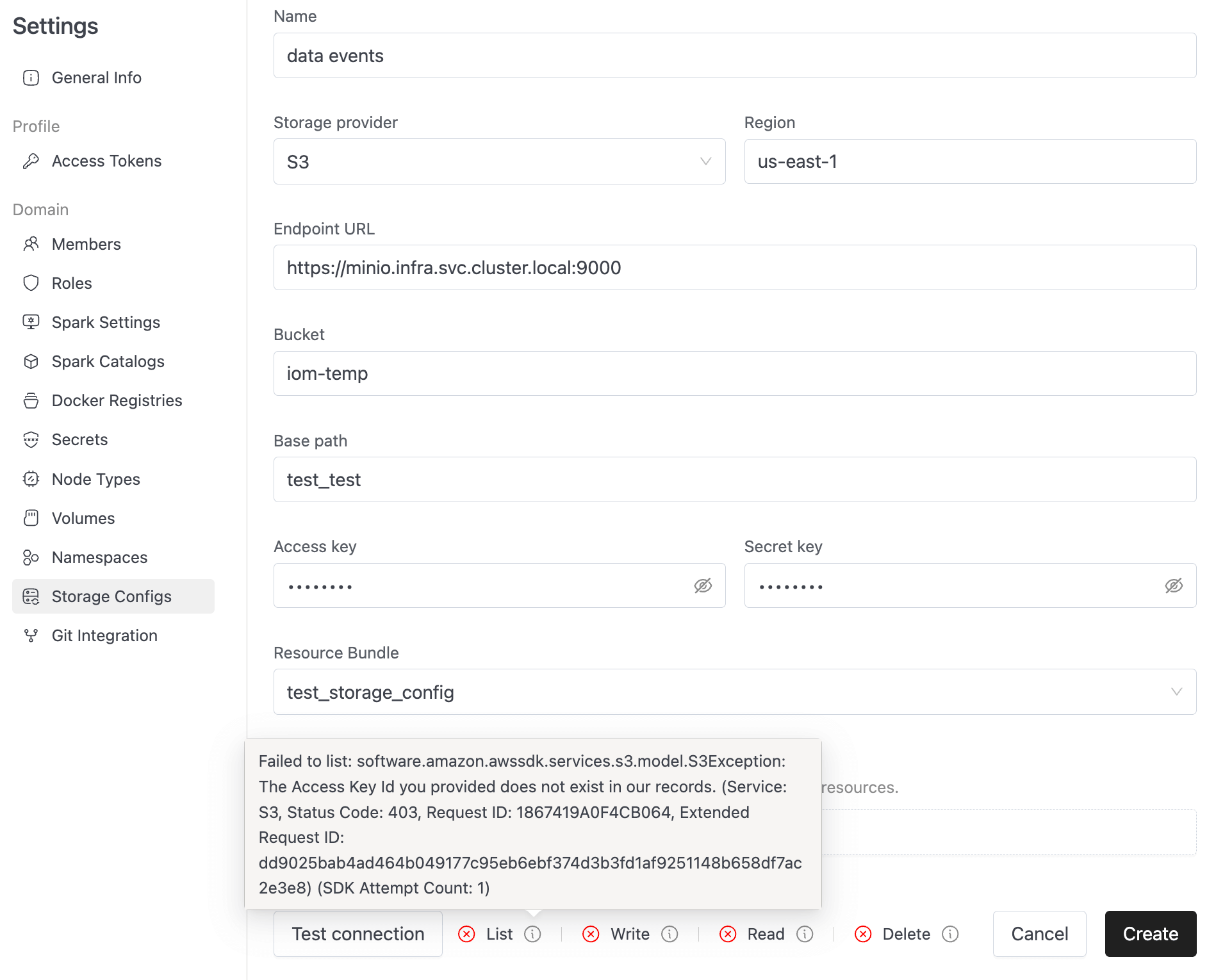
Common connection failures include:
- Invalid credentials: Check your access key and secret key.
- Network issues: Verify the endpoint URL and network connectivity.
- Permission errors: Ensure the credentials have appropriate bucket permissions.
- Bucket access: Confirm the bucket exists and is accessible.
- Region mismatch: Verify the region setting matches your bucket's location.
Managing Storage Configs
Once created, storage configurations can be edited and managed from the Storage Configs list. Each configuration shows its current status and provides options for:
- Editing: Modify configuration parameters.
- Testing: Re-test connections after changes.
- Enabling/Disabling: Control whether the storage config is active.
- Permission Management: Configure access levels (Current only
Consumemanaged via Resource Bundles).
Using Storage Configs
Storage configurations can be used in various places throughout the IOMETE platform, including:
- Worksheets Storage: Store SQL editor worksheets in different storage locations
- Job Artifacts Storage: Store and access job artifacts and outputs (Future)
- Audit and History Logs: Persistent storage for system audit trails and historical data (Future)
Currently, the only usage is for workspaces to store worksheets in different storage locations within the SQL editor. Additional use cases are planned for future releases.