Docker Tag Aliases
Overview
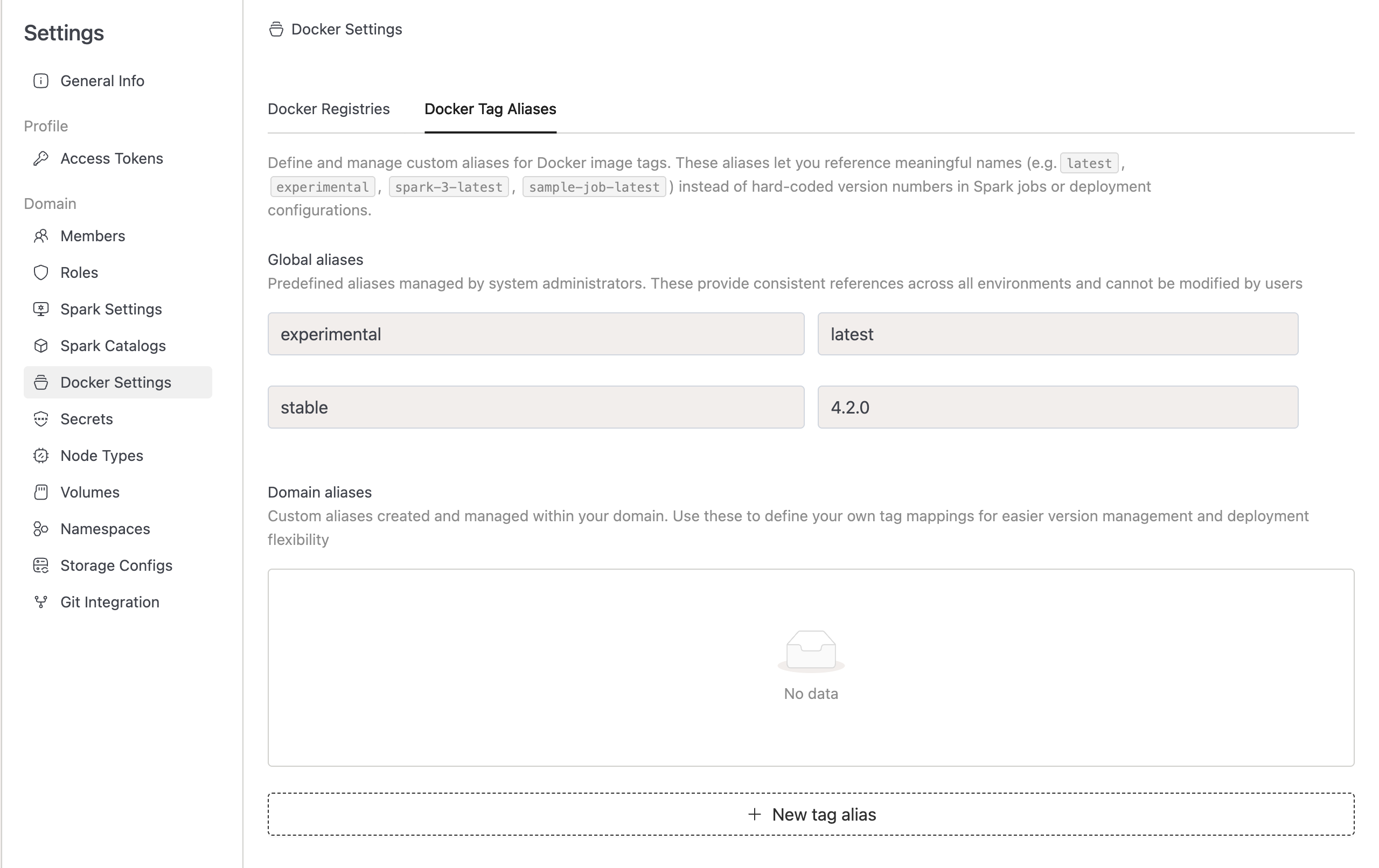
Docker Tag Aliases allow you to define and manage custom aliases for Docker image tags. These aliases let you reference meaningful names (e.g., latest, experimental, spark-3-latest, sample-job-latest) instead of hard-coded version numbers in Spark jobs or deployment configurations. This provides greater flexibility in version management and simplifies updates across your deployment environment.
To view Docker Tag Aliases, navigate to the Settings menu item, switch to the Docker Settings tab, and then select the Docker Tag Aliases tab.
Types of Tag Aliases
Docker Tag Aliases are organized into two categories:
Global Aliases
Global aliases are predefined aliases managed by system administrators. These are defined in HELM files at the time of IOMETE installation and provide consistent references across all environments.
Key characteristics:
- Defined during platform installation
- Cannot be modified by users
- Provide standardized version references across the entire platform
- Ensure consistency across different domains and environments
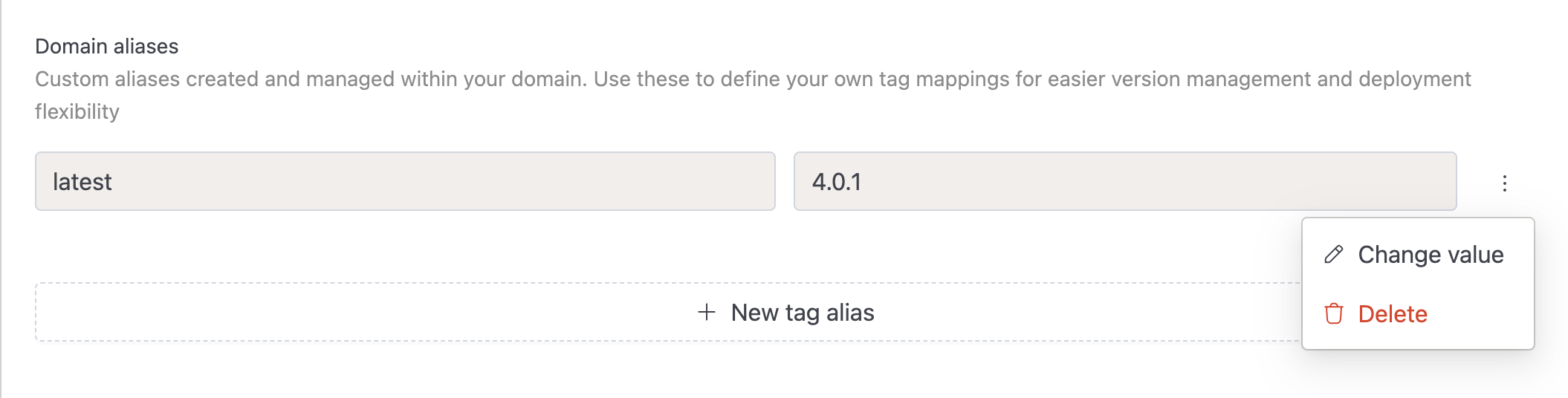
Domain Aliases
Domain aliases are custom aliases that you can create and manage within your specific domain. Use these to define your own tag mappings for easier version management and deployment flexibility.
Key characteristics:
- Created and managed by domain users
- Provide flexibility for domain-specific versioning
- Can be modified or deleted as needed
- Ideal for custom deployments and version control strategies
Managing Domain Tag Aliases
Adding a New Tag Alias
To add a new tag alias:
- Navigate to Settings > Docker Settings > Docker Tag Aliases tab
- Ensure you're in the Domain aliases section
- Click on the New tag alias button
- Enter the alias name (e.g.,
latest,stable,experimental) - Enter the corresponding Docker tag/version (e.g.,
3.9.1,2.1.0) - Click Save to save the tag alias
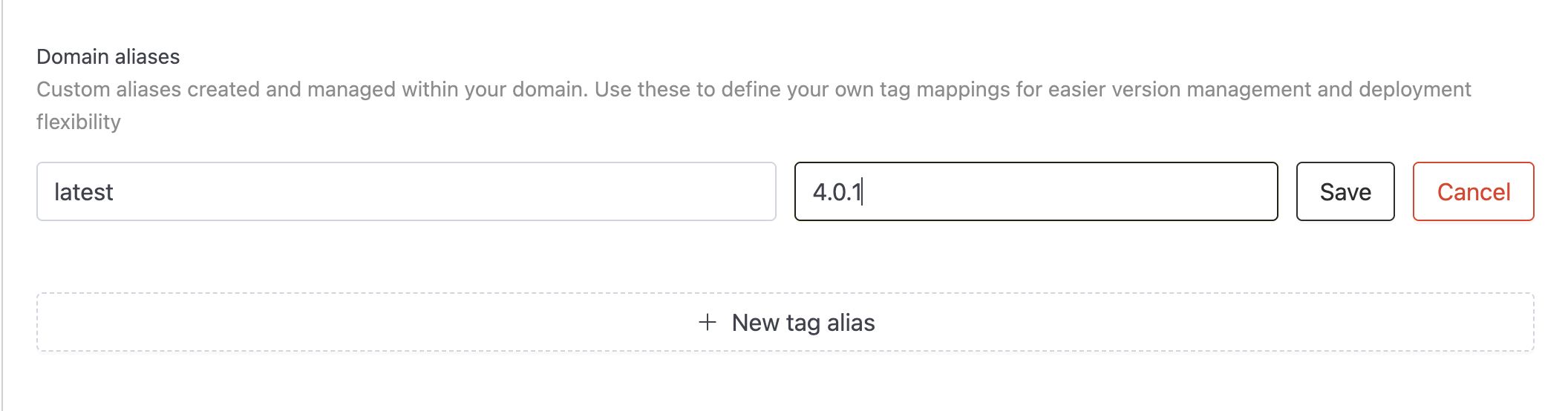
Changing an Alias Value
If you want to update the tag version for an existing alias:
- Locate the alias in the Domain aliases table
- Click on the three dots menu (⋮) next to the alias
- Select Change value
- Enter the new tag version
- Click Save
Using Tag Aliases in Spark Jobs
Tag aliases can be used in Spark jobs to reference Docker images without hard-coding specific version numbers. This makes it easier to update versions across multiple jobs by simply updating the alias mapping.
Syntax
To use a tag alias in a Spark job, reference it using the ${alias_name} syntax in the Docker image field:
iomete.azurecr.io/iomete/spark-py:${stable}
Instead of using a hard-coded version:
iomete.azurecr.io/iomete/spark-py:3.9.1
Steps to Use Tag Aliases
- Navigate to Spark Jobs and create or edit a job
- In the Application section, locate the Docker image field
- Enter the Docker image path with the alias syntax:
- Example:
iomete.azurecr.io/iomete/spark-py:${stable} - Example:
myregistry.io/custom-spark:${latest}
- Example:
- Save and run the job
Benefits
- Easy version management: Update the alias mapping once to affect all jobs using that alias
- Consistent deployments: Use meaningful names like
stableorproductionacross your environment - Simplified rollbacks: Quickly revert to previous versions by updating the alias
- Better organization: Group related versions under meaningful aliases
Best Practices
- Use descriptive alias names: Choose names that clearly indicate the purpose (e.g.,
stable,beta,prod-latest) - Document your aliases: Maintain documentation of which aliases map to which versions
- Test before updating: When changing an alias value, test with a single job before updating production workloads
- Avoid frequent changes: Establish a process for updating aliases to prevent unexpected behavior
- Monitor dependencies: Before deleting an alias, check which resources reference it