MySQL Database Replication Job
Quickly move your MySQL tables to IOMETE Lakehouse using our Spark Job that's simple to configure. All you need to do is provide the settings, and the job will handle the rest. Choose how you want to transfer your data: either a full load or in smaller increments. Scroll down for more details on these sync options.
If you want to make changes, you can copy the job and adjust it however you like.
Deployment
- In the left sidebar menu choose Spark Jobs
- Click on Create
Specify the following parameters (these are examples, you can change them based on your preference):
- Name:
mysql-db-sync - Docker image:
iomete/iomete_mysql_sync:2.0.0 - Main application file:
local:///app/driver.py - Environment variables:
DB_PASSWORD:9tVDVEKp
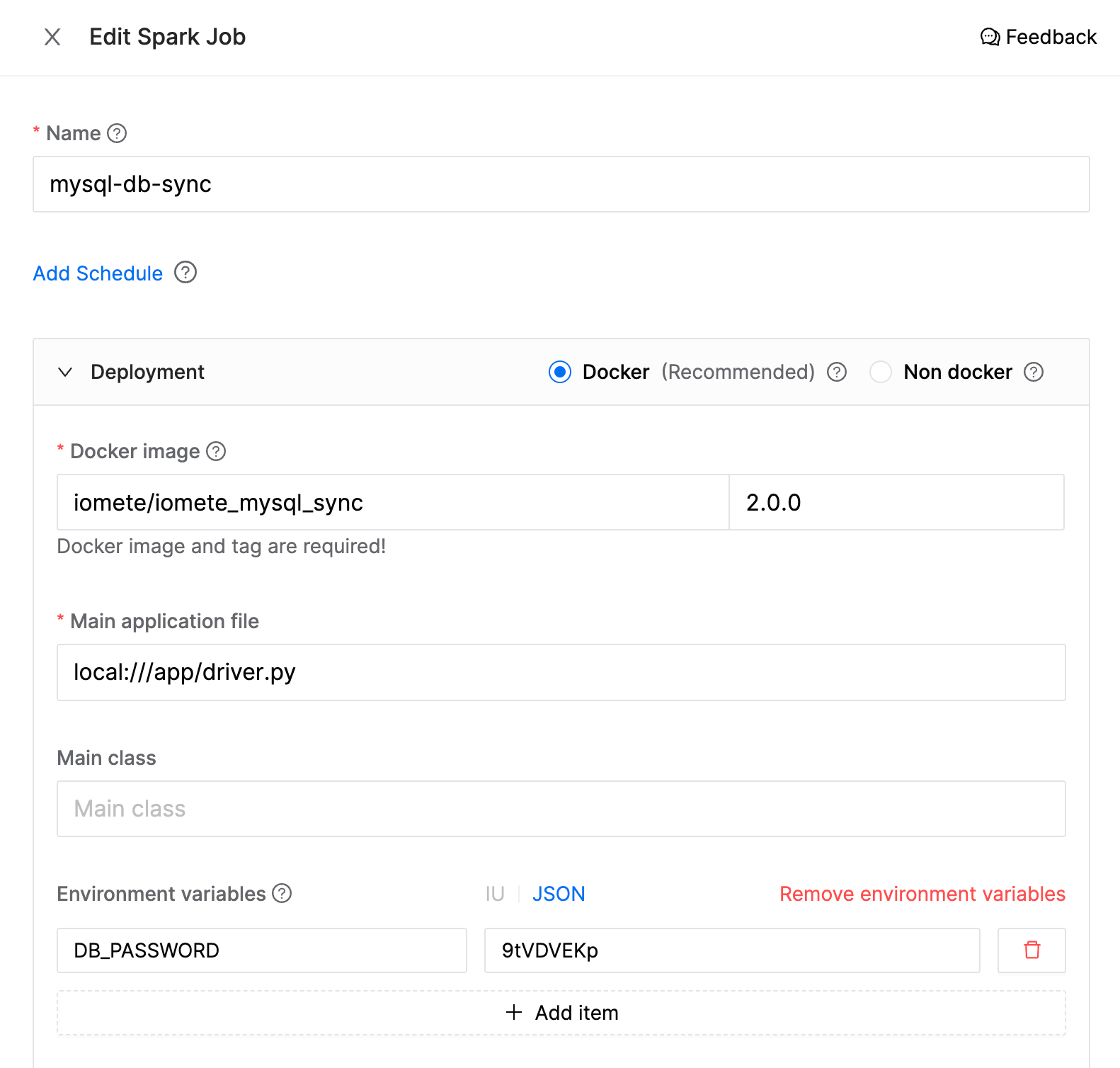

You can use Environment variables to store your sensitive variables like password, secrets, etc. Then you can use these variables in your config file using the ${DB_PASSWORD} syntax.
Config file
The following configuration file is used to set up the syncing of tables from a MySQL database to IOMETE Lakehouse. It specifies the source database connection details and the tables you want to sync.
Use the configuration file below as a template and modify it to fit your needs.
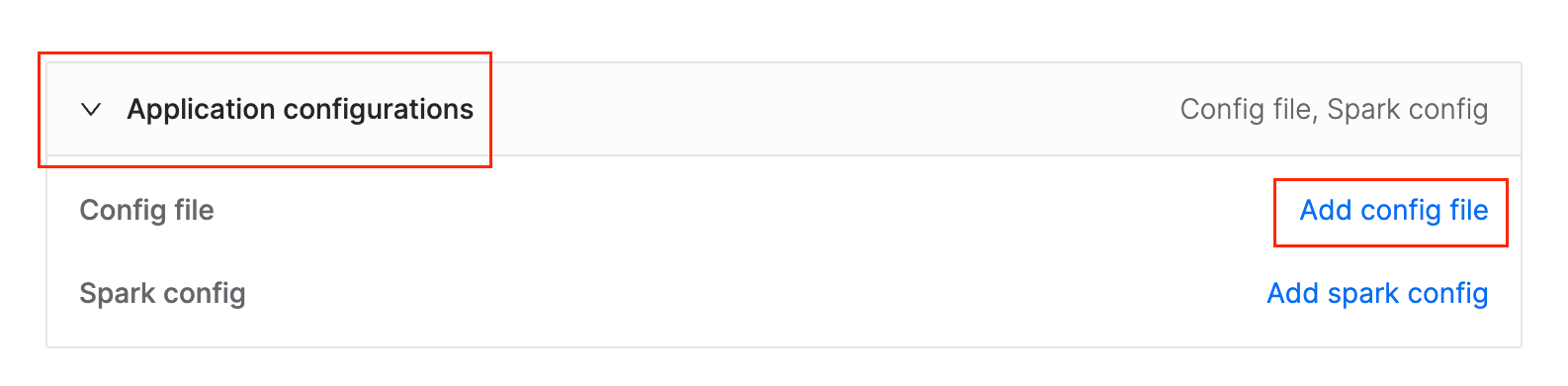
To add config file scroll down and expand Application configurations section and click Add config file and paste following HOCON.

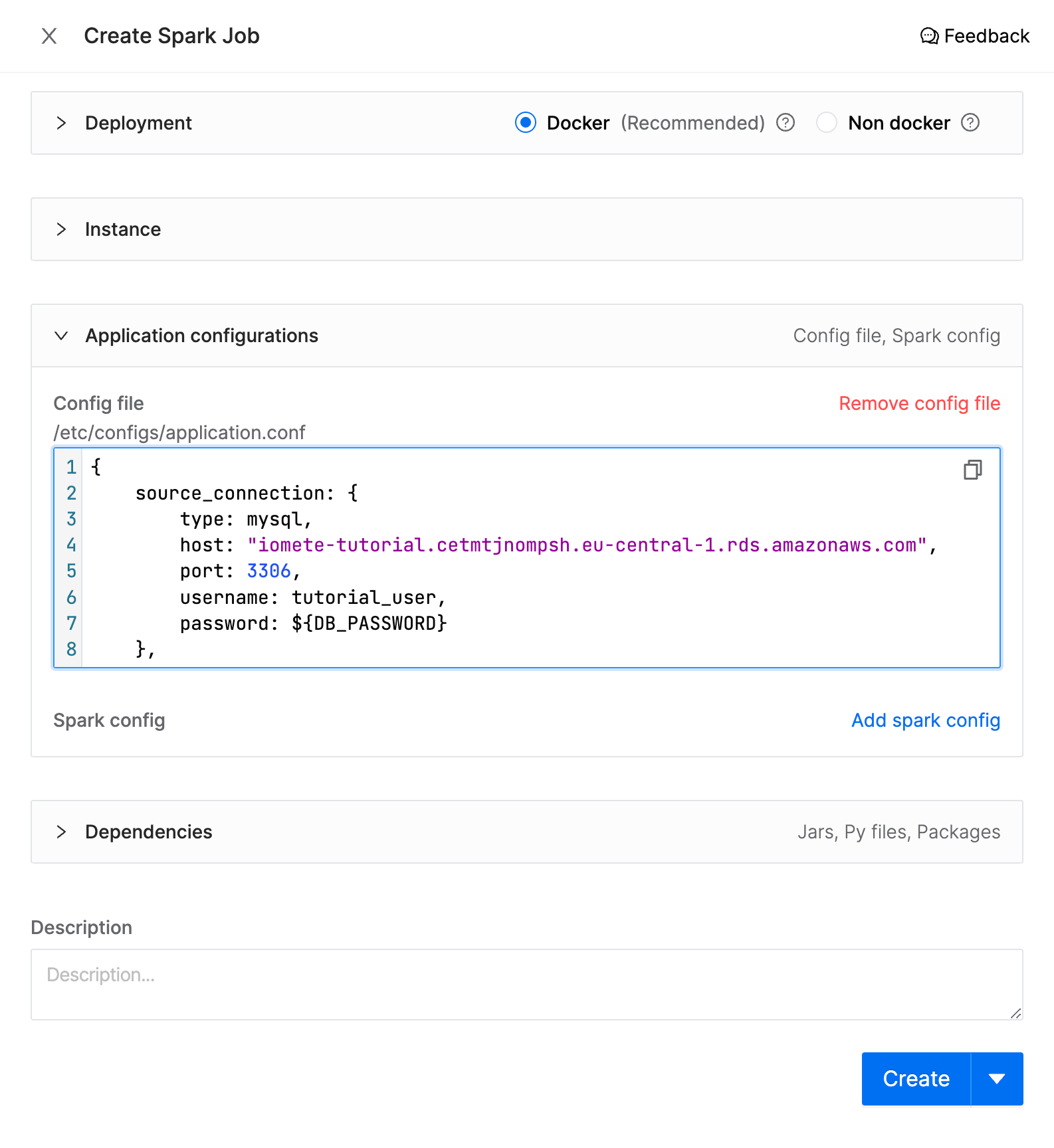

{
source_connection: {
host: "iomete-tutorial.cetmtjnompsh.eu-central-1.rds.amazonaws.com",
port: 3306,
username: tutorial_user,
password: $\{DB_PASSWORD}
},
syncs: [
{
source.schema: employees
source.tables: ["*"]
source.exclude_tables: [departments, dept_manager]
destination.schema: employees_raw
sync_mode.type: full_load
},
{
source.schema: employees
source.tables: [ departments, dept_manager ]
destination.schema: employees_raw
sync_mode.type: full_load
}
]
}
Source Connection
The source_connection object contains the following fields:
- host: The address of the MySQL database. For example,
iomete-tutorial.cetmtjnompsh.eu-central-1.rds.amazonaws.com. - port: The port number for the database connection, usually
3306for MySQL. - username: The username to connect to the database, like
tutorial_user. - password: The password for the database connection. Here,
${DB_PASSWORD}is a variable that you can set in the Environment variables section.
The shown MySQL database is a sample database that you can use to test out IOMETE.
Syncs Array
The syncs array contains one or more objects that specify what to sync:
Sync Object Fields
- source.schema: The schema in the source MySQL database you want to sync from, such as
employees. - source.tables: An array of table names you want to sync. Use
["*"]to sync all tables. - source.exclude_tables: [Optional] An array of table names you want to exclude from syncing.
- destination.schema: The schema in the IOMETE Lakehouse where the data will be stored, like
employees_raw. - sync_mode.type: The type of sync.
full_load- Read everything in the source and overwrites whole table at the destination at each sync.incremental_snapshot- It creates the snapshot of table in the destination and only move the newly inserted and updated records. While writing to IOMETE it uses merge statement. This mode requires two additional parameters:identification_column- can be id or other primary key column that will be used on merge statementtracking_column- column that will be used to track the where it should continue to get data from the source table. For example, if you want to sync only the records that were inserted or updated after the last sync, you can use theupdated_atcolumn as thetracking_column. The column should be increasing and updated with each insert or update.
This example syncs all tables from the employees schema, except for the salaries table, into the employees_raw schema in IOMETE Lakehouse.
{
source.schema: employees
source.tables: ["*"]
source.exclude_tables: [salaries]
destination.schema: employees_raw
sync_mode.type: full_load
}
This example syncs only the departments and dept_manager tables from the employees schema into the employees_dep schema in IOMETE Lakehouse.
{
source.schema: employees
source.tables: [departments, dept_manager]
destination.schema: employees_raw
sync_mode.type: full_load
}
This example does incremental snapshot sync of the salaries table from the employees schema into the employees_raw schema in IOMETE Lakehouse.
{
source.schema: employees
source.tables: [salaries]
destination.schema: employees_raw
sync_mode: {
type: incremental_snapshot
identification_column: id
tracking_column: updated_at
}
}
- source.schema:
employees - source.tables:
[salaries] - destination.schema:
employees_raw - sync_mode.type:
incremental_snapshot
This example syncs only the departments and dept_manager tables from the employees schema into the employees_dep schema in IOMETE Lakehouse.
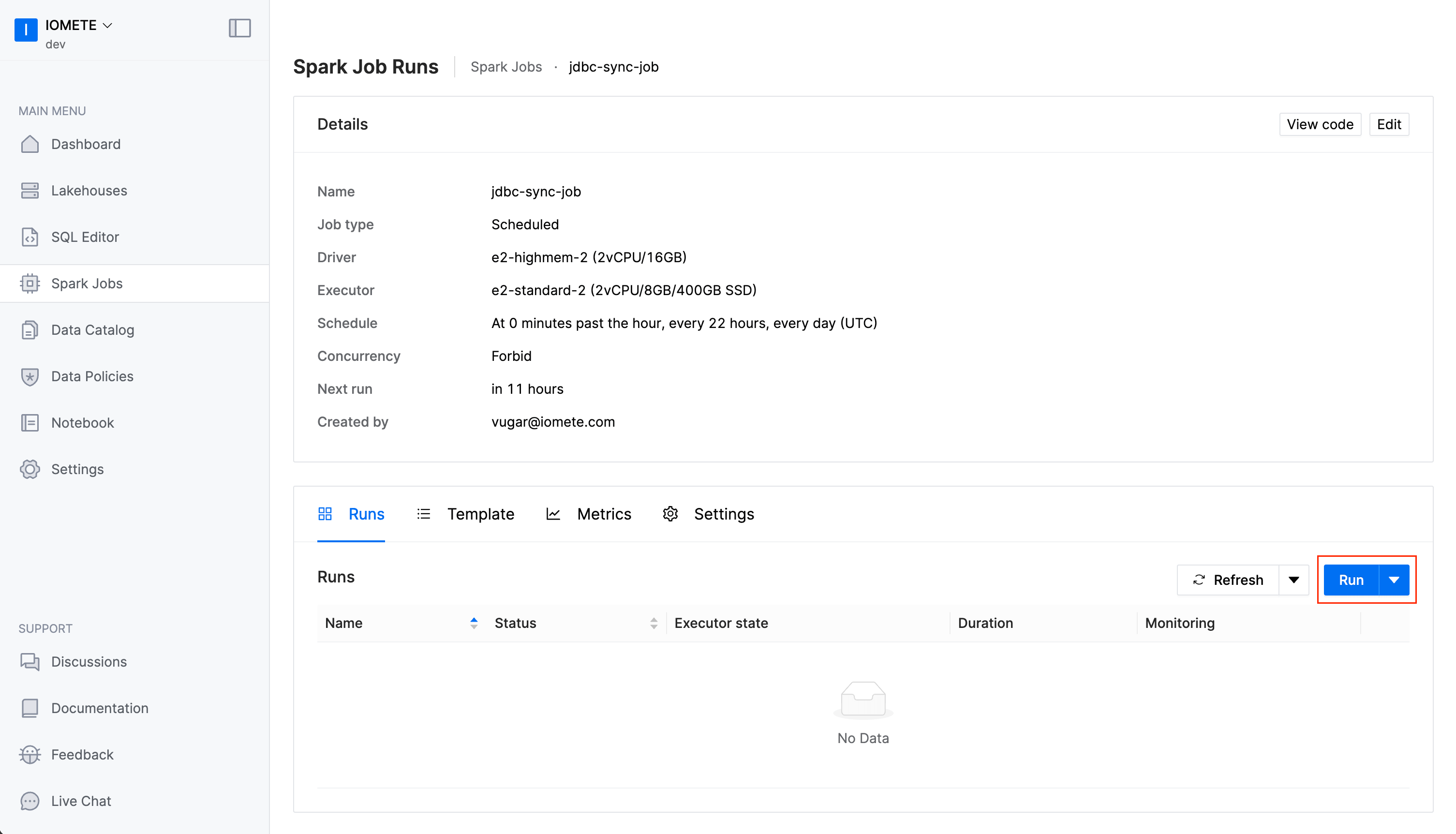
Run the job
You can trigger the job manually by clicking on the Run button.
You can also schedule the job to run periodically. To do this, edit spark job and set the Schedule parameter.

Github
You can find source code of IOMETE: MySQL Sync (DB Replication) in github. View in Github