Architecture Overview
Architecture Overview
IOMETE is a Data Lakehouse Platform that provides a unified data platform for AI and Analytics. It is built on top of Apache Spark, Iceberg, and Kubernetes. IOMETE is designed to be a scalable, reliable, and high-performance platform for data processing and analytics.
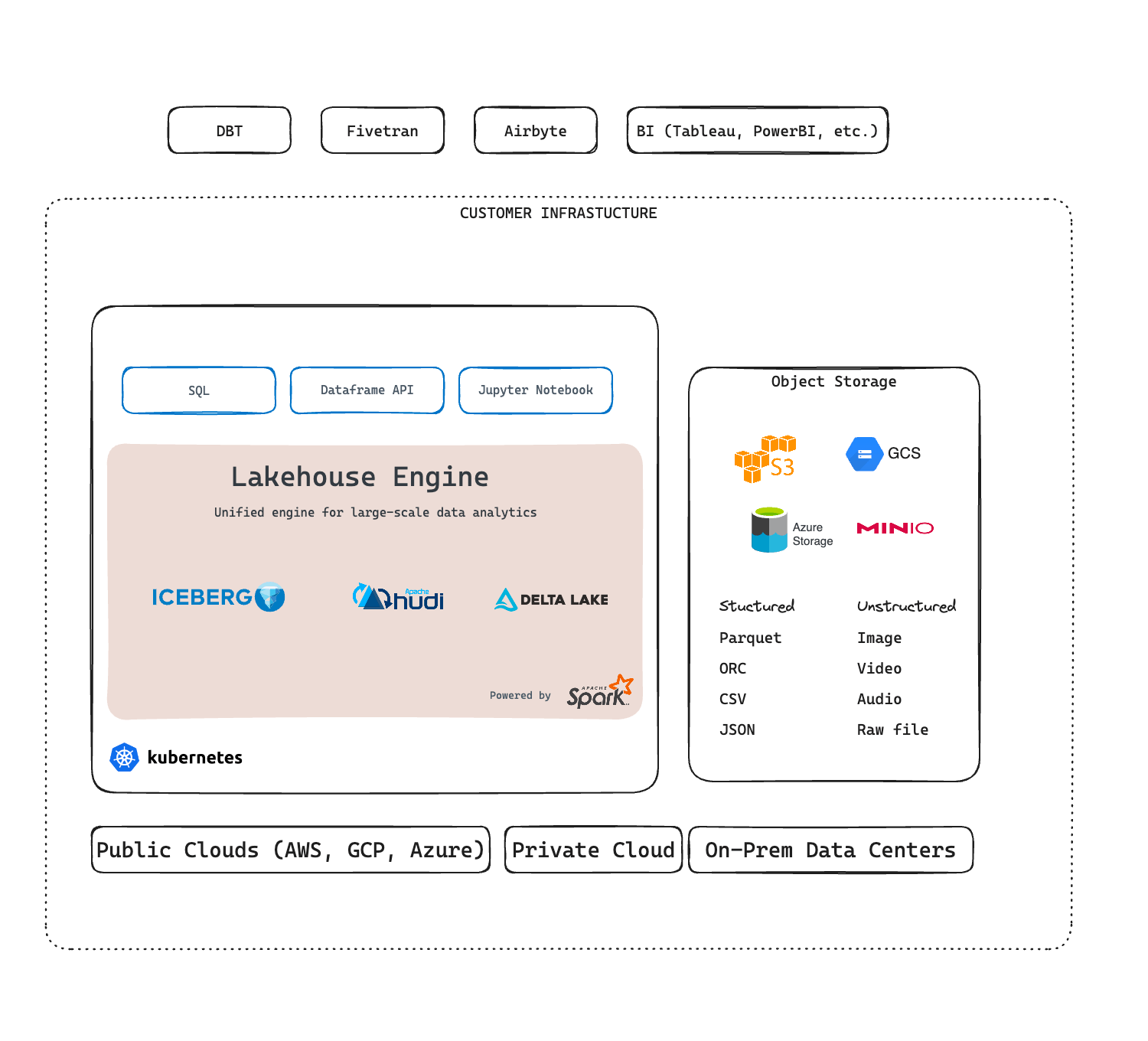

High-Level Architecture
IOMETE runs on top of Kubernetes, which can be deployed on any cloud provider or on-premises data center. IOMETE uses Object Storage (e.g., AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage, Minio) as the storage layer for data.
Inside Kubenetes, IOMETE is deployed and provides a set of services that are used to manage data, run Spark jobs, and provide a SQL interface to query and process data.
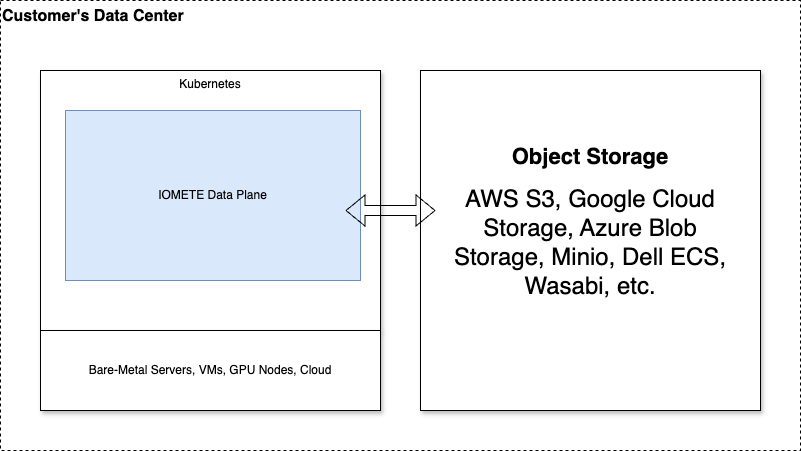

Inside Data Plane - IOMETE Services
If we dive deeper into the IOMETE services, we can see the following components:
- Microservices: IOMETE is built on top of microservices architecture. Each service is responsible for a specific task, such as managing metadata, running Spark jobs, or providing a SQL interface. In the diagram below, bluish boxes represent microservices.
- Workloads: These are the actual workloads based on Spark Engine that serves different purposes.
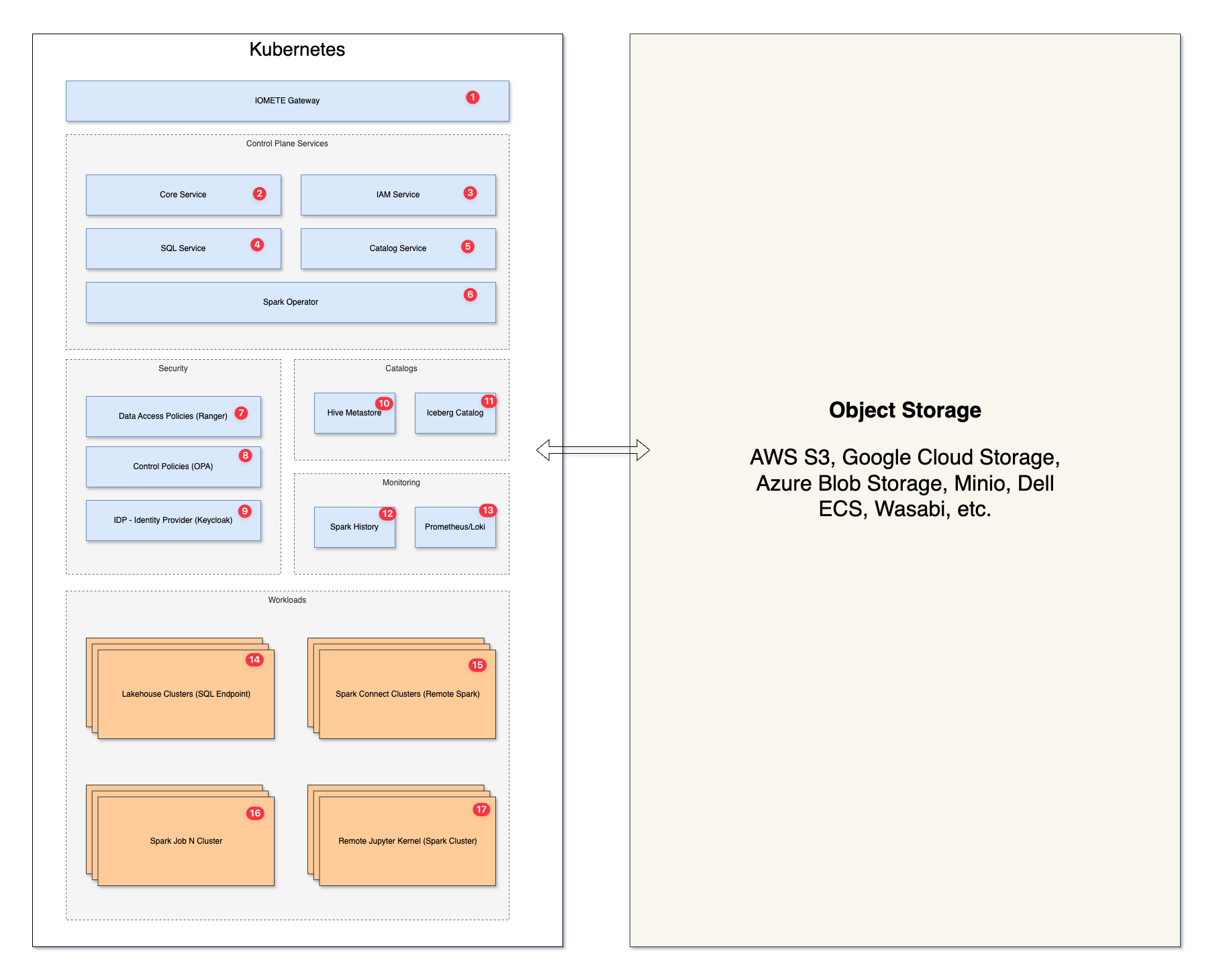

Microservices
1. IOMETE Gateway: IOMETE Gateway is the entry point to the IOMETE platform. It's a reverse proxy that routes requests to the appropriate microservices.
Control Plane Services
- 2. Core Service: Core Service is the main service that manages metadata, scheduling, and orchestration of workloads.
- 3. IAM Service: IAM Service is responsible for managing users, groups, and permissions, as well as managing other IDP integrations, such as LDAP, SAML, etc. See Identity and Access Management.
- 4. SQL Service: SQL Service provides REST API for SQL and also provides a backend for the SQL Editor. See SQL Editor.
- 5. Catalog Service: Catalog Service is a backend service for Data Catalog. Which provides metadata management, data discovery, tagging, and lineage.
- 6. Spark Operator: Spark Operator is a Kubernetes operator that manages all Spark Workloads. It schedules, monitors, and manages the lifecycle of Spark clusters.
Security
- 7. Data Access Policies (Ranger): Data Access Policies is a service that manages data access policies for databases, tables, and columns. It provides a consistent way to manage permissions for groups or users. See Data Security.
- 8. Control Policies (OPA): Control Policies is a service that manages control policies for the platform. It provides a way to manage platform-level policies, such as who can create lakehouses, who can run Spark jobs, etc. See Control Policies.
- 9. IDP - Identity Provider (Keycloak): IDP is a service that manages user storage, authentication, and integration powered by Keycloak.
Catalogs
- 10. Hive Metastore: Hive Metastore is a service that manages metadata for Parquet, CSV, JSON, Hive Tables, etc. It provides a way to store metadata for Hive tables and partitions.
- 11. Iceberg Catalog: Iceberg Catalog is a service that manages metadata for Iceberg Tables.
Monitoring
- 12. Spark History: Spark History is a service that provides Spark job history and monitoring. It's useful for debugging and monitoring completed Spark jobs.
- 13. Prometheus/Loki/Grafana: Prometheus, Loki, and Grafana are services that provide monitoring, logging, and visualization for the platform and workloads.
Workloads
- Lakehouse Clusters: Lakehouse Clusters are the clusters that provide SQL interface that can be connected from any SQL client, BI tools (e.g., Tableau, PowerBI), DBT, or any other tool that supports JDBC/ODBC. See Lakehouses.
- Spark Jobs: Spark Jobs are the Spark jobs that are submitted to the Spark Engine for execution. See Spark Jobs.
- Jupyter Remote Kernel: Jupyter Remote Kernel is the Jupyter Kernel that can be connected from any Jupyter Notebook to execute code remotely (e.g., ML training, data processing). See Jupyter Remote Kernel.