Optimize CPU and memory usage for Kubernetes deployments
Running applications in Kubernetes is incredibly powerful, but it also comes with its challenges. One common issue developers face is effectively managing CPU and memory usage. If resources aren't managed wisely, deployments can become sluggish, unstable, or even crash. Here are, real-world steps you can take to optimize your Kubernetes deployments and keep your clusters running efficiently.
Step 1: Understanding Your Application's Resource Needs
First things first—before you optimize, you need a clear picture of your application's resource consumption.
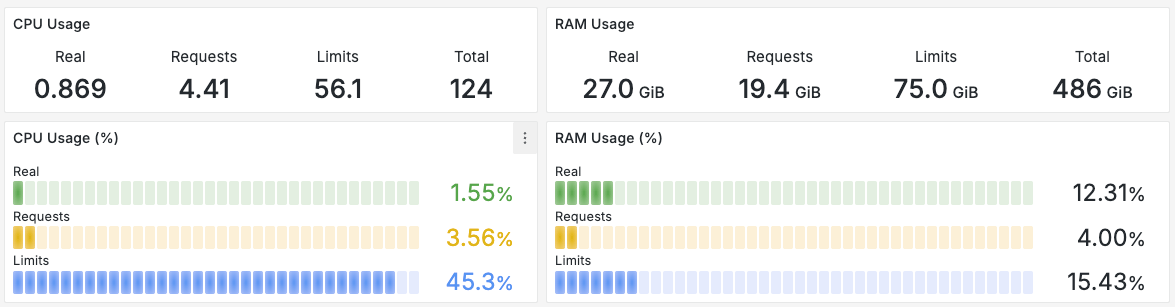
- Monitor Your Current Usage: Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to visualize how your pods consume CPU and memory over time.
- Analyze Peak Usage: Identify periods of peak usage to set realistic resource limits.
Step 2: Define Resource Requests and Limits
Kubernetes provides two key parameters:
- Requests: Minimum guaranteed resources Kubernetes reserves for a pod.
- Limits: Maximum resources a pod can consume.
Here's a simple YAML snippet:
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "0.5"
limits:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "1"
Aim for requests that closely reflect your application's typical usage, while limits should prevent excessive resource consumption.
Step 3: Use Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)
If your application experiences fluctuating traffic, HPA can scale pods automatically based on resource usage:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: my-app-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: my-app-deployment
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 75
This ensures optimal resource usage, adding pods when necessary and scaling back during quiet periods.
Step 4: Implement Node Affinity and Taints
Make sure pods are scheduled efficiently using node affinity and taints:
- Node Affinity: Ensures pods are placed on the right nodes, maximizing resource usage.
- Taints and Tolerations: Control precisely which pods can run on certain nodes.
Example:
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: high-performance
operator: In
values:
- "true"
Step 5: Optimize Your Container Images
Slim down your container images to reduce startup times and memory footprint:
- Use minimal base images (like Alpine Linux).
- Remove unnecessary packages and dependencies.
- Regularly update images to patch security vulnerabilities.
Step 6: Regularly Review and Adjust
Optimization is a continuous process:
- Regularly review resource usage and performance.
- Adjust requests, limits, and scaling policies as your application evolves.
- Stay proactive—early intervention can save significant resources and downtime.
Conclusion
Efficient Kubernetes resource management doesn't require magic—just consistent monitoring, thoughtful planning, and incremental adjustments. Follow these practical steps, and you'll maintain a balanced, cost-effective, and stable Kubernetes environment that's ready to scale seamlessly as your application grows.