AWS Terraform Advanced Settings
Using AWS Profiles
If you're using named profiles in the AWS Credentials file, you need to export the profile to the environment before running Terraform.
For example, if you have the following profile in your AWS Credentials file (usually located at ~/.aws/credentials):
[default]
...
[my_profile]
aws_access_key_id = ...
aws_secret_access_key = ...
You can export the profile to the environment using the following command:
export AWS_PROFILE=my_profile
Then run Terraform as usual
For detailed information see: Named profiles for the AWS CLI
Public Access Restriction
By default, the EKS API (Kubernetes cluster API) is accessible from anywhere. However, if you need to restrict public access to the EKS API for security or compliance reasons, follow these steps:
Add the following code to the Terraform script:
module "data-plane-aws" {
# omitting other parameters for brevity
kubernetes_public_access_cidrs = ["your_ip_range/mask"] # <- add this line
}
To access the cluster, you need to specify your_ip_range/mask, which represents your IP address. Omitting this will prevent you from accessing the cluster. However, this step can be skipped if you're connecting via the AWS Private Network, for instance, through a bastion host.
If you have any questions or need assistance, please don't hesitate to contact our support team.
Define additional administrators
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) is an Amazon Web Services product that allows administrators to create, delete and control keys that encrypt data stored in AWS databases and products.
AWS KMS can be accessed within AWS Identity and Access Management by selecting the "Encryption Keys" section or by using the AWS KMS command-line interface or software development kit
IOMETE customer-stack Terraform module will use or create a KMS key only who run the Terraform code if additional administrator ARN`s not added. (AWS KMS see:https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/overview.html )
Adding an additional administrator to the system will grant them access to manage Kubernetes resources in EKS. By default, only the creator of the resources has access to Kubernetes. To add additional administrators, include their user Amazon Resource Names (ARNs) when running the Terraform code. It is important to note that when adding additional ARNs, the creators must include their own ARNs in the list to ensure that they retain access to the resources.
To add additional administrators, add the following code to the Terraform script:
module "data-plane-aws" {
# omitting other parameters for brevity
additional_administrators = ["arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/your_arn", "arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/user2", "arn:aws:iam::1234567890:user/user3"]
}
Do not forget to add your user ARN to the list of additional administrators. Otherwise, you will lose access to the resources.
Saving terraform state
Terraform's default behavior is to store its state file locally, which works well for individual projects. However, for team collaboration and to avoid losing the state file, it's advisable to use remote state storage. Here are some options for storing Terraform state remotely:
Please, check the Terraform documentation for more information on Terraform backends.
Using EBS encryption
If your AWS account is configured to use EBS encryption, you need to add users to the KMS key policy to allow IOMETE data-plane to access the key.
This is necessary for the IOMETE data-plane to access to EBS storage, which allows it to attach EBS volumes to the nodes within the IOMETE data-plane.
Please follow these steps to add users to the KMS key policy:
Identify the KMS key
First you need to determine which key is used for encrypting EBS volumes, you can follow these instructions to find the appropriate key:
- Select the appropriate Region in the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to the EC2 service by clicking on the 'EC2 Dashboard' in the upper menu.


- In the right-side menu, locate the
Account attributessection and click onEBS encryption. - On the EBS encryption page, you will find the
Default encryption keysection.

- Note down the key displayed as the Default encryption key.
Add users to the KMS key policy
Once you have identified the key, you need to grant access to the IOMETE Data-plane service for this key. This will enable the IOMETE Data-plane to perform necessary operations on the encrypted EBS volumes.
To add a user/role to a KMS key using the AWS Management Console, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to the AWS KMS service.
- Click on Customer managed keys in the left-hand menu.
- Select the KMS key you want to manage.


- Locate the Key details section or navigate to the specific tab where the "Key users" tab is available.
- Click on the Key users tab.
- Click on "Add" and enter 'iomete' in the search/filter box to narrow down the list of available roles.
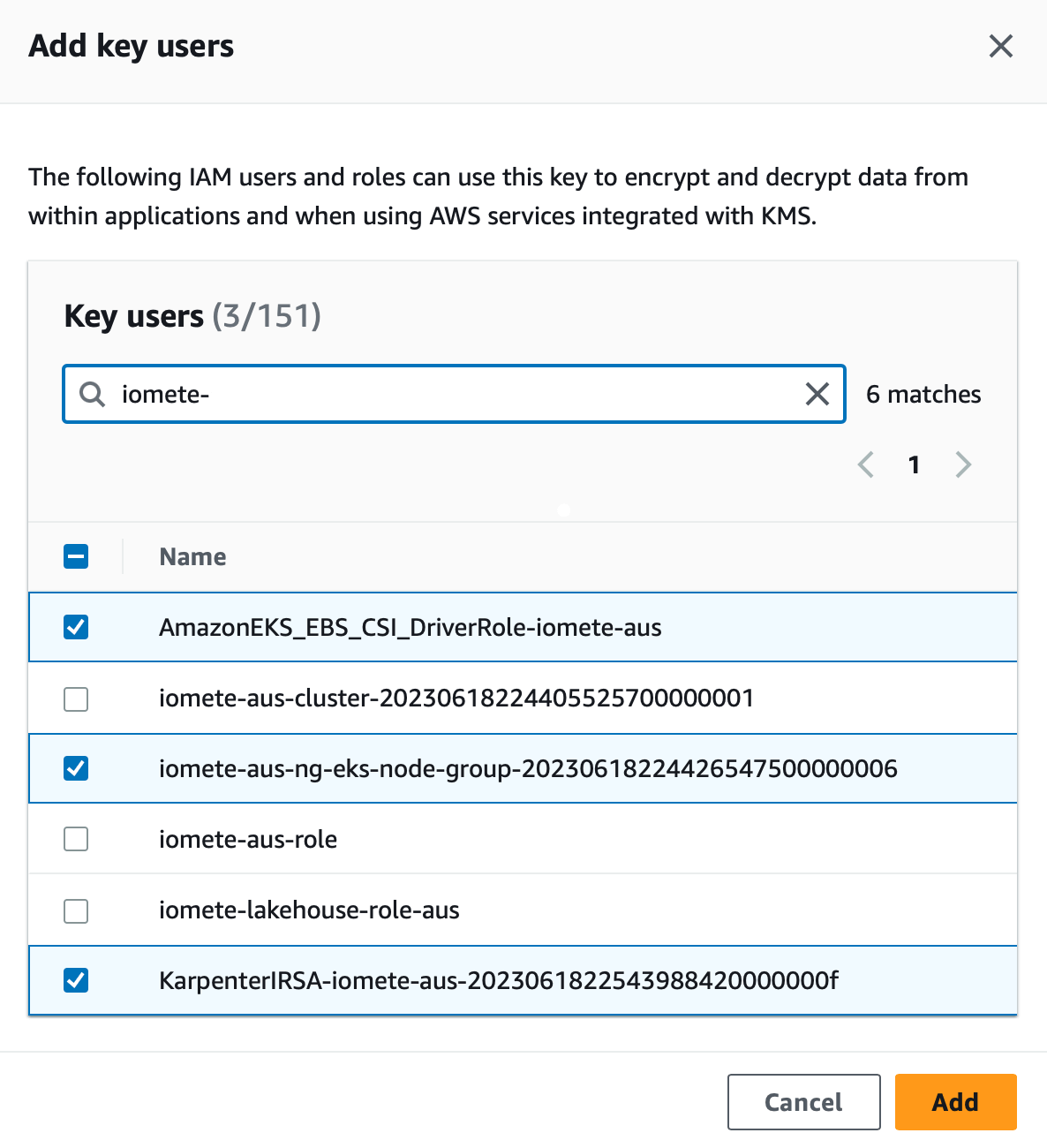

- Add the following roles to the key policy:
iomete-{cluster_id}-ng-eks-node-group-202...KarpenterIRSA-iomete-{cluster_id}-202...AmazonEKS_EBS_CSI_DriverRole-{cluster_id}

- Click on Save changes to save the modifications to the KMS key policy.
Now, IOMETE Data Plane should be able to attach EBS volumes to the nodes.