Data lake benefits 2023

Introduction
A data lake is a data repository where all enterprise data is stored, including structured data from relational databases or data warehouses, unstructured or semi-structured data (such as CSV files, log files, emails, and documents), and digital content (such as images, audio files, and video files). In this article we will cover the basics of data lakes.
Data lakes
A data lake is a centralized repository of structured and unstructured data. Data lakes provide a scalable platform for two of the 4 V’s (Volume, Velocity, Veracity, and Variety) to generate value from raw unstructured data.
Data lakes are designed to provide a single source of truth for data analysis while decoupling the source applications. This raw data can then be processed and analyzed without any negative performance impact on the source/operational system/application, using a variety of different tools and techniques such as data mining, machine learning, and analytics. Data lakes can store data from a variety of sources, including social media, sensors, and log files. They can also be used to store data from traditional enterprise systems, such as databases and data warehouses. One of the key benefits of using a data lake is that it allows you to store data in its raw, unprocessed form. This means that you can store all your data, even if you don't yet know how you will use it in the future.
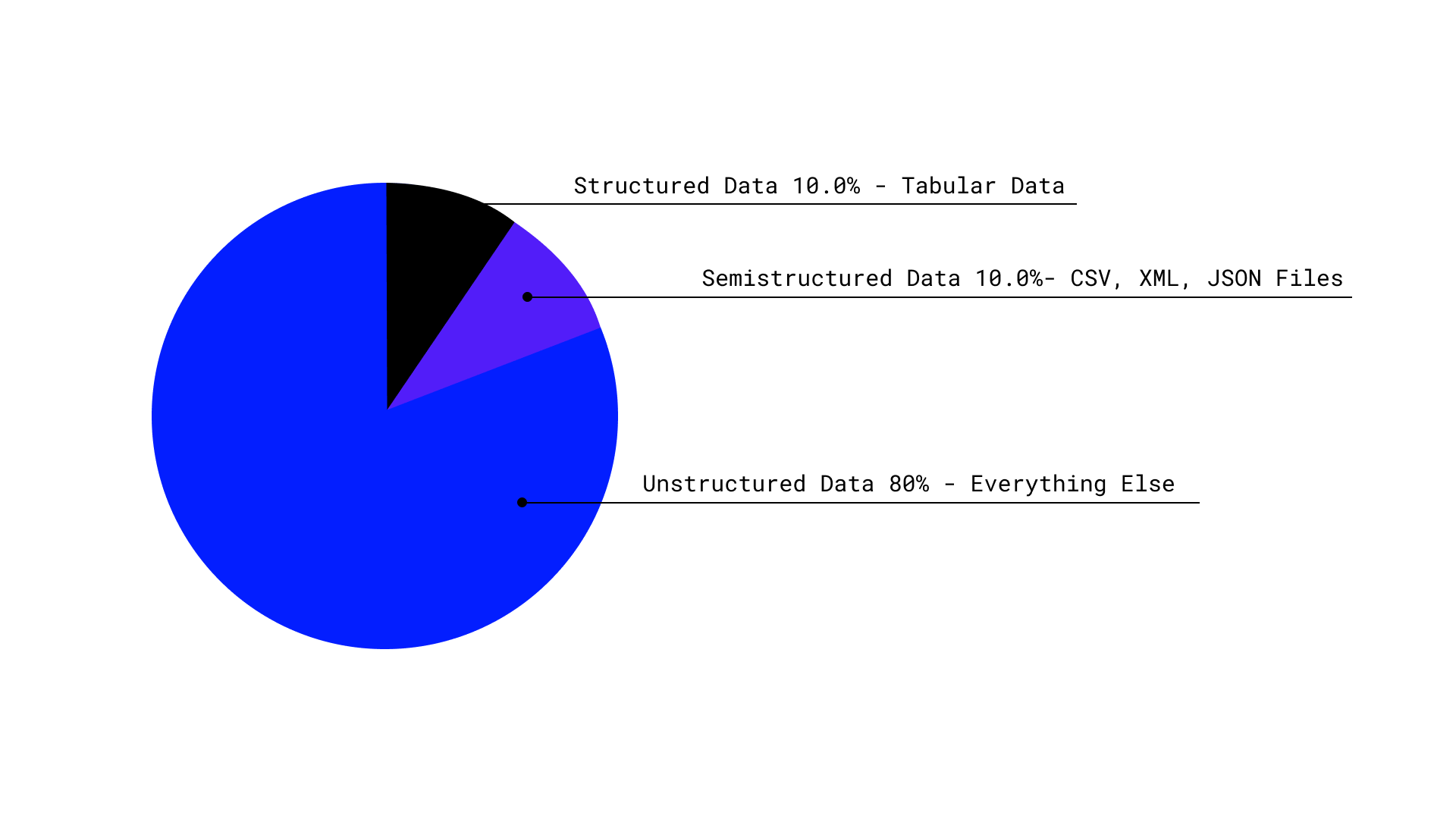
Pie shows the estimate of the world’s data by structure | source: Datamation
When was the data lake invented?
One of the earliest references to the concept of a data lake can be found in a 1998 paper by James Dixon, the founder of Pentaho, in which he described the idea of a "data reservoir" as a place to store all of an organization's data, structured and unstructured, in its raw form. Since then, the concept of a data lake has evolved and has been adopted by a wide range of organizations as a way to store and manage large amounts of data for analysis and decision-making. Data lakes have become particularly popular in recent years with the growth of cloud computing, making it easier and more cost-effective for organizations to store and process large amounts of structured or unstructured data.

What are the benefits of a data lake?
There are several benefits to using a data lake:
- One source of truth for analytical use cases: A data lake provides a centralized repository for storing all your data, structured and unstructured, in one place. This makes it easy to store and manage large amounts of data.
- Flexibility: Data lakes allow you to store data in its raw, unprocessed form. This means that you can store data without worrying about the structure or how you will use it, making it possible to store data for later analysis and uncover insights that you might not have found otherwise. This makes data lakes perfect for ML and AI uses cases.
- Scalability: Data lakes are designed to store large amounts of data, making it easy to scale up as your data grows.
- Cost-effective: Data lakes can be more cost-effective than traditional data warehousing solutions for certain use cases as costly ETL can be mostly avoided. You can durably store a nearly unlimited amount of data using Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake, Minio, and Google Cloud Storage.
- Enhanced analytics: A data lake makes it possible to perform a wide range of analytics on your data, including batch processing, real-time stream processing and interactive analysis. This makes it easier to gain insights and make data-driven decisions.
When is the right time to use a data lake?
Data lakes are typically introduced when organizations need scalable, flexible, cost-effective, and secure ways to capture, store, organize, and access increasing amounts of data of various types and sizes. They are ideal for scenarios in which structured data generated by databases and applications need to be combined with unstructured data such as log files or social media feeds.
How IOMETE can help you?
IOMETE provides a “data lake on steroids”: the data lakehouse. The IOMETE data lakehouse combines the best of data lakes and data warehouses. It combines the scalability and flexibility of a data lake with the structure and organization of a data warehouse. It allows organizations to store large amounts of raw data in a cost-effective way and perform analytics on that data - including machine learning and AI - while also providing a structured environment for BI use cases.