On-premise Analytics Platform case study
Background: A large organization operates an on-premise/self hosted storage that processes vast amounts of customer and internal data for various purposes, including payments, billing, and operations and sales optimization. The organization faces challenges with data silos, performance bottlenecks, and the need to accommodate different analytics tools and frameworks.
Challenges:
- Data Silos: Data is stored in different formats and locations across the organization, leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Performance: As data volumes grow, the performance of analytics queries using their existing tightly coupled database system is degrading.
- Tool Diversity: The organization uses a variety of analytics tools, including SQL-based queries, machine learning libraries, and custom scripts. Each tool requires different data formats and access methods.
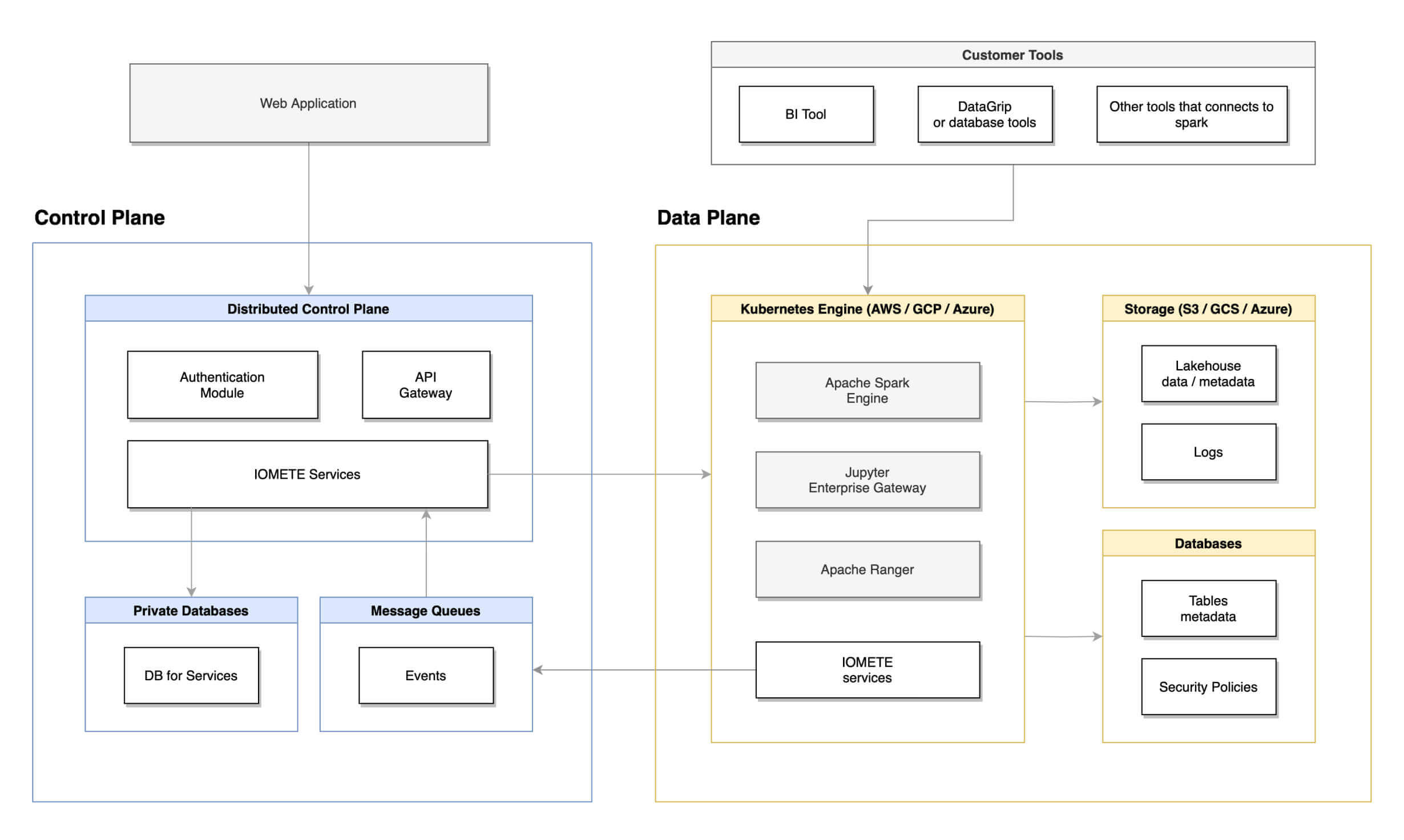
Solution: Single Kubernetes Cluster
Let's go step-by-step on how IOMETE solves a challange:
Step 1: Kubernetes Cluster
- The organization sets up a single Kubernetes cluster for managing all analytics workloads.
- Kubernetes provides orchestration, scalability, and resource management capabilities for different types of analytics tasks.
Step 2: Data Transformation and Open Formats
- Data stored in various formats across the organization is transformed and standardized into open table formats like Apache Iceberg.
- The organization adopts a data lake approach, where all data is stored in shared storage accessible from the Kubernetes cluster using network-attached storage (NAS).
Step 3: Access Control and Security
- Access control and security measures are implemented at both the storage (NAS) and compute (Kubernetes) layers. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized users and processes can access sensitive patient data.
Step 4: Integration with Analytics Tools
- The Kubernetes cluster is configured to integrate with popular analytics tools:
- SQL-based analytics tools can use Kubernetes pods running SQL query engines.
- Machine learning workloads can be orchestrated as Kubernetes jobs using GPU-enabled nodes.
- Custom scripting and data processing tasks can be run as Kubernetes pods using general-purpose containers.
Benefits:
- Reduced Data Silos: All data is stored in a centralized data lake using open formats, eliminating data silos and making it accessible to various analytics tools.
- Consolidated Management: All analytics workloads are managed within a single Kubernetes cluster, simplifying resource allocation and management.
- Improved Performance: Kubernetes allows for scaling resources based on demand, improving query and processing performance.
- Flexibility: The organization can use the right tool for the job within the Kubernetes cluster, whether it's SQL queries, machine learning, or custom scripting, without copying or moving data.
- Security and Compliance: Access controls are enforced consistently, ensuring patient data remains secure and compliant with healthcare regulations.
- Scalability: The architecture allows for easy scaling of compute resources to handle growing data volumes and changing analytics requirements.
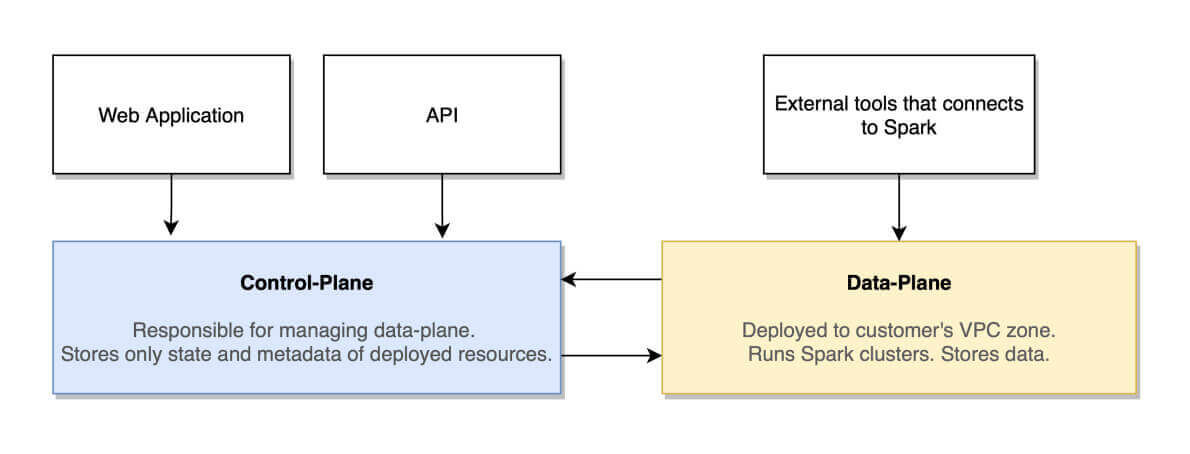
By consolidating analytics workloads into a single Kubernetes cluster while maintaining a centralized data lake, the organization achieves greater flexibility, performance, and data accessibility while simplifying management. This approach can be particularly beneficial for organizations looking to streamline their analytics infrastructure in an on-premises environment.
Conclusion
By separating storage and compute the organization achieves greater flexibility, performance, and data accessibility while maintaining strict security and compliance standards. This use case demonstrates how the separation of storage and compute can benefit organizations with diverse analytics needs in an on-premises environment.